|
原文:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/658343628
之前讲述了大模型精度(FP16,FP32,BF16)详解与实践,本文围绕1.模型不同精度下显存占用情况;2.模型不同精度之间如何转换,两个问题进行一个简单的实践。模型不同精度下显存占用
以显卡NVIDIA A40 48G,模型用llama-2-7b-hf为例[1],这个模型的保存的精度通过查看模型文件的congfig.json可以看到是"torch_dtype": "float16"。
首先打印相关的版本和显卡信息:
import transformers
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
# 打印版本号
print("transformers version:", transformers.__version__)
print("torch version:", torch.__version__)
# 检查系统中是否有可用的 GPU
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# 获取可用的 GPU 设备数量
num_devices = torch.cuda.device_count()
print("可用 GPU 数量:", num_devices)
# 遍历所有可用的 GPU 设备并打印详细信息
for i in range(num_devices):
device = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(i)
print(f"\nGPU {i} 的详细信息:")
print("名称:", device.name)
print("计算能力:", f"{device.major}.{device.minor}")
print("内存总量 (GB):", round(device.total_memory / (1024**3), 1))
else:
print("没有可用的 GPU")
# 结果
transformers version: 4.32.1
torch version: 2.0.1+cu117
可用 GPU 数量: 1
GPU 0 的详细信息:
名称: NVIDIA A40
计算能力: 8.6
内存总量 (GB): 44.4
然后用transformers加载模型,精度设为float16:
# 加载模型
model_name = "/path/to/llama-2-7b-hf" # 你模型存放的位置
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="cuda:0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
加载模型后,查看一下模型的总参数:
total_parameters = model.num_parameters()
print("Total parameters in the model:", total_parameters)
# 结果
Total parameters in the model: 6738415616 # 6.73B
以float16进行加载,也就是每个参数16个bit,2个byte,计算一下这么多参数应该占多少显存:
# 计算每个参数的大小(以字节为单位)
size_per_parameter_bytes = 2
# 计算模型在显存中的总空间(以字节为单位)
total_memory_bytes = total_parameters * size_per_parameter_bytes
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
total_memory_gb = total_memory_bytes / (1024**3)
print("Total memory occupied by the model in MB:", total_memory_gb)
# 结果
Total memory occupied by the model in GB: 12.551277160644531
接着看一下,现在的显存占用:
# 计算模型的显存占用
memory_allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device='cuda:0')
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
memory_allocated_gb = memory_allocated / (1024**3)
print("Memory allocated by the model in GB:", memory_allocated_gb)
# 结果
Memory allocated by the model in GB: 12.582542419433594
看一下显卡的占用nvidia-smi:
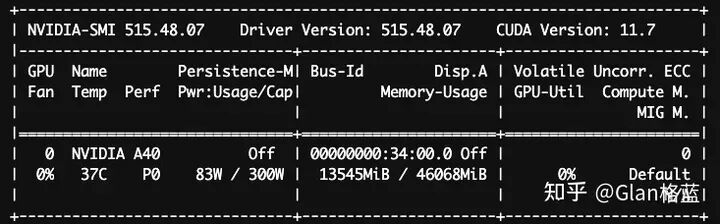 可以看到这三个数值是接近一致的(稍微差一点的原因:框架torch以及transformers本身、GPU的本身缓存等等)。
以上是在float16下加载的,同理看一下在float32下加载的情况,只贴结果了:
# 加载模型float32
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="cuda:0", torch_dtype=torch.float32)
......
# 结果
Total memory occupied by the model in GB: 25.102554321289062
Memory allocated by the model in GB: 25.165069580078125
显卡的占用nvidia-smi:
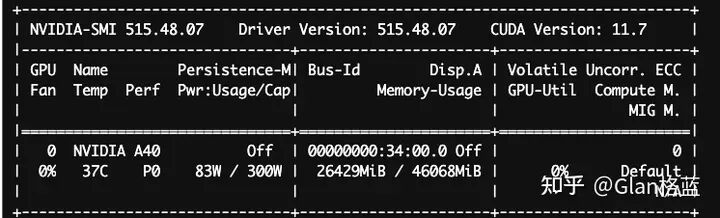 再看一下bfloat16下的结果:
# 加载模型float32
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="cuda:0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
......
# 结果
Total memory occupied by the model in GB: 12.551277160644531
Memory allocated by the model in GB: 12.582542419433594
显卡的占用nvidia-smi:
 可以看到bfloat16和float16占用的显存是完全一样的。
模型不同精度之间如何转换
从huggingface下载的llama-2-7b-hf模型,通过查看模型文件的congfig.json可以看到是"torch_dtype": "float16",那为何加载的时候可以指定float32和bfloat16呢?是如何转化的呢?
是torch在做数据类型的转换,在加载模型时torch内置了转换函数将模型的每一个参数转换类型,如下:
# 对应float32
def float(self: T) -> T:
r"""Casts all floating point parameters and buffers to ``float`` datatype.
.. note::
This method modifies the module in-place.
Returns:
Module: self
"""
return self._apply(lambda t: t.float() if t.is_floating_point() else t)
# 对应float16
def half(self: T) -> T:
r"""Casts all floating point parameters and buffers to ``half`` datatype.
.. note::
This method modifies the module in-place.
Returns:
Module: self
"""
return self._apply(lambda t: t.half() if t.is_floating_point() else t)
# 对应bfloat16
def bfloat16(self: T) -> T:
r"""Casts all floating point parameters and buffers to ``bfloat16`` datatype.
.. note::
This method modifies the module in-place.
Returns:
Module: self
"""
return self._apply(lambda t: t.bfloat16() if t.is_floating_point() else t)
上述函数的使用也可以加载完模型后,手动转化模型,看一下以float32加载转化为float16:
# 以float32加载
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="cuda:0", torch_dtype=torch.float32)
# 计算模型的显存占用
memory_allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device='cuda:0')
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
memory_allocated_gb = memory_allocated / (1024**3)
print("Memory allocated by the model in GB:", memory_allocated_gb)
# 转为float16
model.half()
# 计算模型的显存占用
memory_allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device='cuda:0')
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
memory_allocated_gb = memory_allocated / (1024**3)
print("Memory allocated by the model in GB:", memory_allocated_gb)
# 结果
Memory allocated by the model in GB: 25.165069580078125
Total memory occupied by the model in GB: 12.551277160644531
同样的,以float16加载转化为float32:
# 以float16加载
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="cuda:0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
# 计算模型的显存占用
memory_allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device='cuda:0')
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
memory_allocated_gb = memory_allocated / (1024**3)
print("Memory allocated by the model in GB:", memory_allocated_gb)
# 转为float16
model.float()
# 计算模型的显存占用
memory_allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(device='cuda:0')
# 将字节转换为更常见的单位(GB)
memory_allocated_gb = memory_allocated / (1024**3)
print("Memory allocated by the model in GB:", memory_allocated_gb)
# 结果
Memory allocated by the model in GB: 12.582542419433594
Total memory occupied by the model in GB: 25.165069580078125
转换函数底层是C++(CPU)和CUDA(GPU)实现转化逻辑的:
举一个将单精度浮点数(float32)转换为半精度浮点数(float16)的例子。
假设有一个单精度浮点数二进制为0 10000000 10010001111010111000011表示的十进制值为3.1400。
符号位:
指数位:
尾数位:
合并符号、指数和尾数:
转换后的半精度浮点数二进制表示对应的十进制值约为3.140625。
看一下torch的结果:
import torch
# 创建一个单精度浮点数的张量
float_tensor = torch.tensor([3.14], dtype=torch.float32)
# 将张量转换为半精度浮点数
half_tensor = float_tensor.half()
# 打印转换后的张量及其数据类型
print("Original Tensor:\n", float_tensor)
print("Half-Precision Tensor:\n", half_tensor)
# 结果
Original Tensor:
tensor([3.1400])
Half-Precision Tensor:
tensor([3.1406], dtype=torch.float16)
继续看一下将半精度浮点数(float16)转换为单精度浮点数(float32),假设有一个半精度浮点数:0 01101 1010000000,其十进制值为约3.14,float16为3.140625。
符号位:
指数位:
尾数位:
合并符号、指数和尾数:
转换后的单精度浮点数表示的十进制值约为3.140625,torch中:
import torch
# 创建一个半精度浮点数的张量
float_tensor = torch.tensor([3.14], dtype=torch.float16)
# 将张量转换为单精度浮点数
single_tensor = float_tensor.float()
# 打印转换后的张量及其数据类型
print("Original Tensor:\n", float_tensor)
print("Single-Precision Tensor:\n", single_tensor)
# 结果
Original Tensor:
tensor([3.1406], dtype=torch.float16)
Single-Precision Tensor:
tensor([3.1406])
通过上面的例子也可以看出float32精度是要高于float16的。以上就是模型不同精度下显存占用情况以及模型不同精度之间如何转换两个问题的一个简单实践。
|