ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 0.544px;text-wrap: wrap;color: rgb(0, 0, 0);background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);visibility: visible;line-height: normal;">本文将针对仅编码器Transformer架构(Decoder-Only Transformer)的模型必备显存优化技术 KV Cache 进行讲解。

KV Cache 简介
KV Cache 是大模型推理性能优化的一个常用技术,该技术可以在不影响任何计算精度的前提下,通过空间换时间的思想,提高推理性能。
KV Cache 诞生的背景
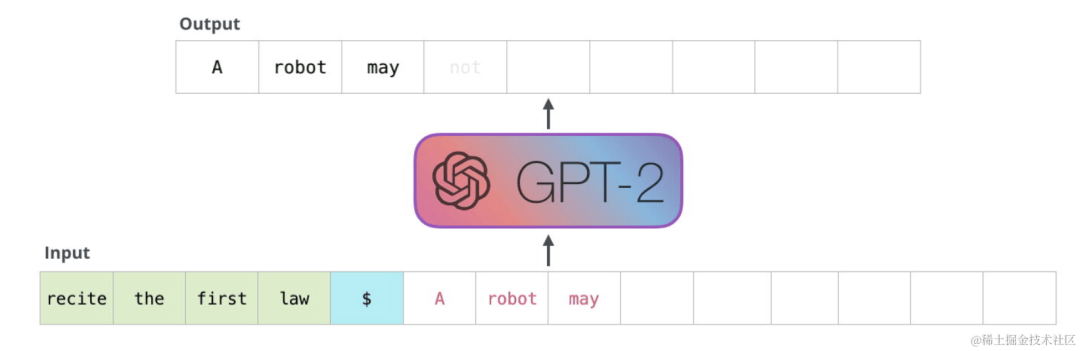
对于仅编码器Transformer架构的模型的推理,我们给一个输入文本,模型会输出一个回答(长度为 N),其实该过程中执行了 N 次推理过程。即类 GPT 的仅编码器模型一次推理只输出一个token,输出的 token 会与输入 tokens 拼接在一起,然后作为下一次推理的输入,这样不断反复直到遇到终止符。
针对一个仅编码器Transformer架构的模型,假设用户输入为“recite the first law”,模型续写得到的输出为“A robot may not ”,模型的生成过程如下:
- 将“ecite the first law”输入模型,得到每个token的注意力表示。使用“law”的注意力表示,预测得到下一个token为“A”(实际还需要将该注意力表示映射成概率分布logits,为了方便叙述,我们忽略该步骤)。
- 将“A”拼接到原来的输入,得到“recite the first law A”,将其输入模型,得到注意力表示,使用“A”的注意力表示,预测得到下一个token为“robot”。
- 将“robot”拼接到原来的输入,依此类推,预测得到“robot”,最终得到“recite the first law A robot may not”
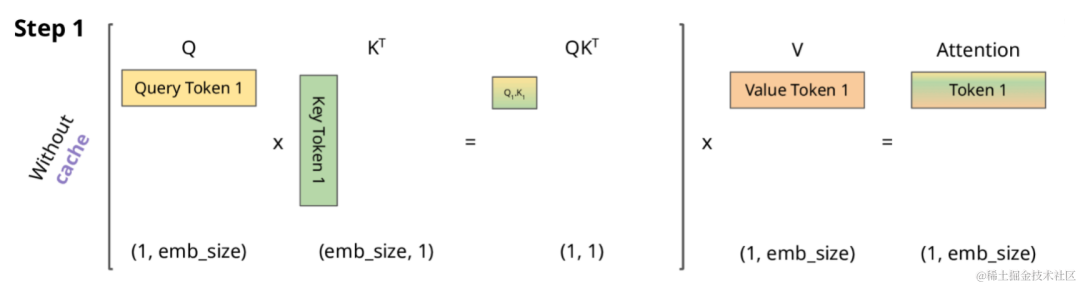
仅编码器Transformer架构的自回归模型为带 Masked 的 Self Attention。因此,在没有KV Cache的情况下,其计算过程如下所示。
正常情况下,Attention的计算公式如下:
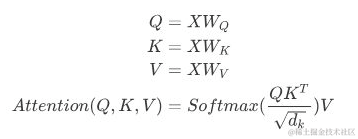
为了看上去方便,我们暂时忽略scale项,因此,Attention的计算公式如下所示(softmaxed 表示已经按行进行了softmax):
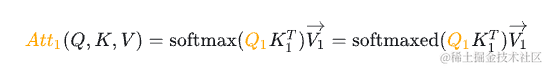
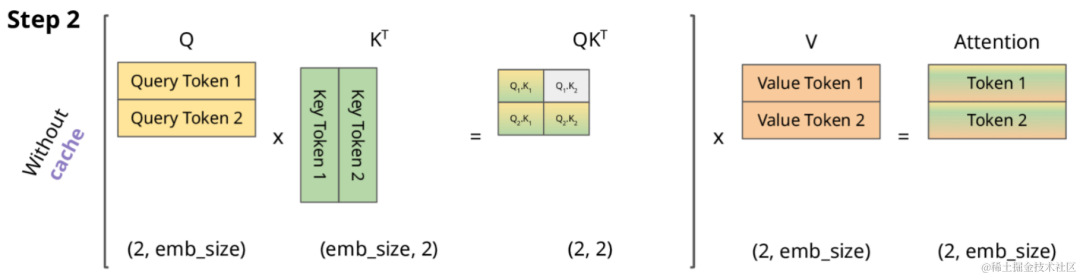
当变为矩阵时,softmax 会针对行进行计算,详细如下(softmaxed 表示已经按行进行了softmax):
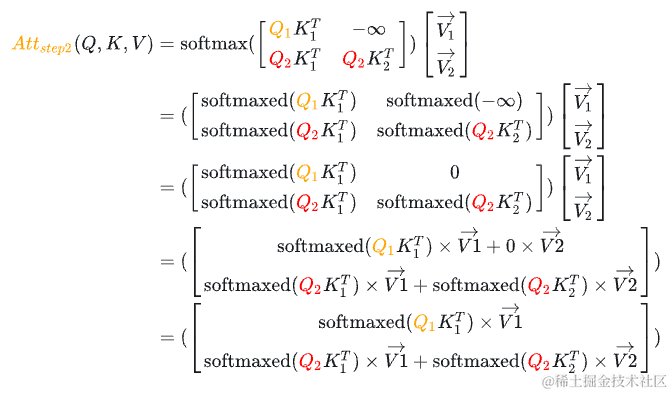
其中,表示 Attention 的第一行,表示 Attention 的第二行。
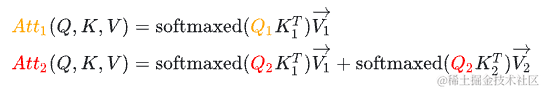
对于,由于这个值会mask掉,你会发现, 在第二步参与的计算与第一步是完全一样的,并且 参与计算Attention时也仅仅依赖于 ,与 毫无关系。
对于, 参与计算Attention时也仅仅依赖于 ,与 毫无关系。
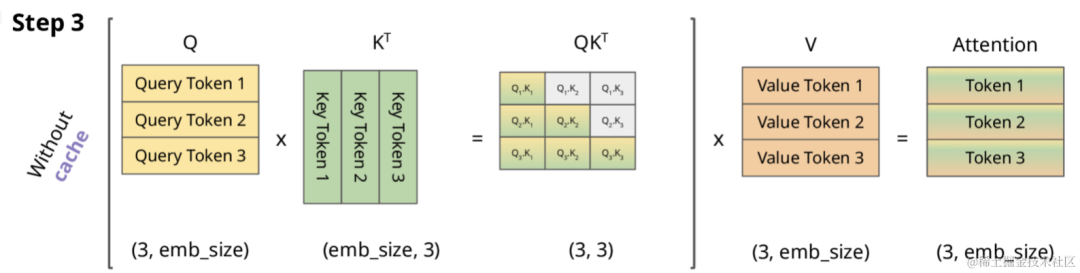
其计算方式如 Step2 所示。
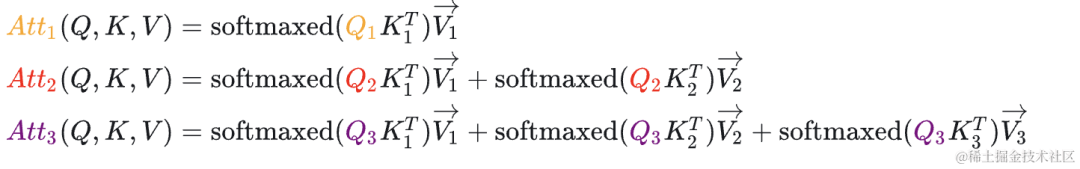
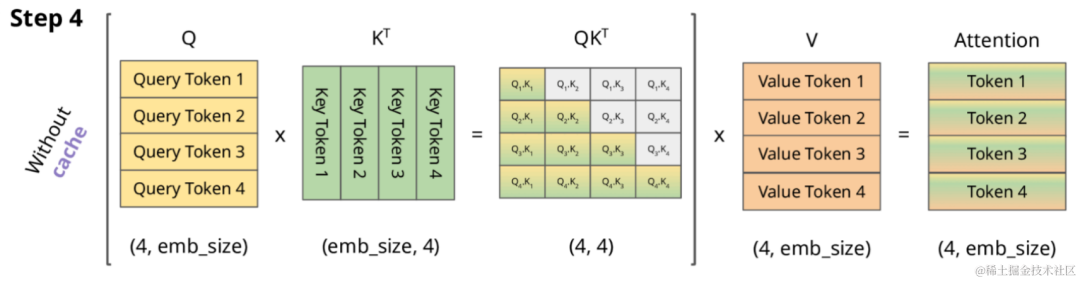
其计算方式如 Step2 所示。
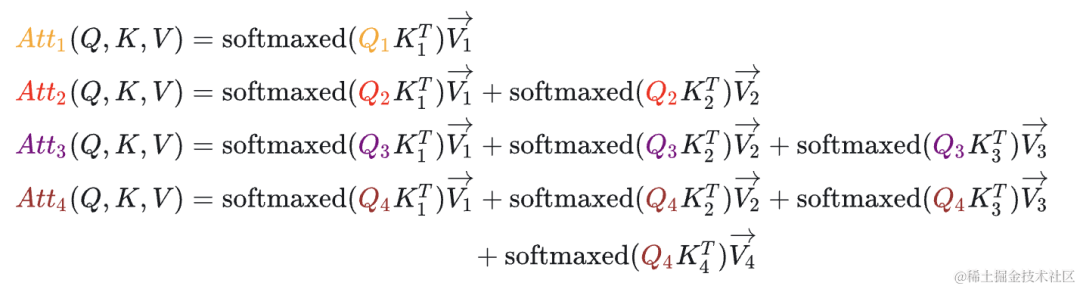
对于, 参与计算Attention时也仅仅依赖于。
看上面图和公式,我们可以得出以下结论:
- 当前计算方式存在大量冗余计算,每一次生成新的Token都需要计算之前的KV。
- 的计算过程中,主要与 有关。 参与计算Attention时也仅仅依赖于。
- 每一步中,其实只需要根据 计算 就可以,之前已经计算的Attention完全不需要重新计算。但是K和V是全程参与计算的,所以这里我们需要把每一步的 K、V 缓存起来。
KV Cache 步骤
正是因为 Self Attention 中带 Masked ,因此,在推理的时候,前面已经生成的 Token 不需要与后面的 Token 产生 Attention ,从而使得前面已经计算的 K 和 V 可以缓存起来。
一个典型的带有 KV cache 优化的生成大模型的推理过程包含了两个阶段:
1.预填充阶段:输入一个prompt序列,为每个transformer层生成 key cache 和 value cache(KV cache)。
2.解码阶段:使用并更新KV cache,一个接一个地生成token,当前生成的token词依赖于之前已经生成的token。
预填充阶段计算过程如下:

解码阶段计算过程如下:

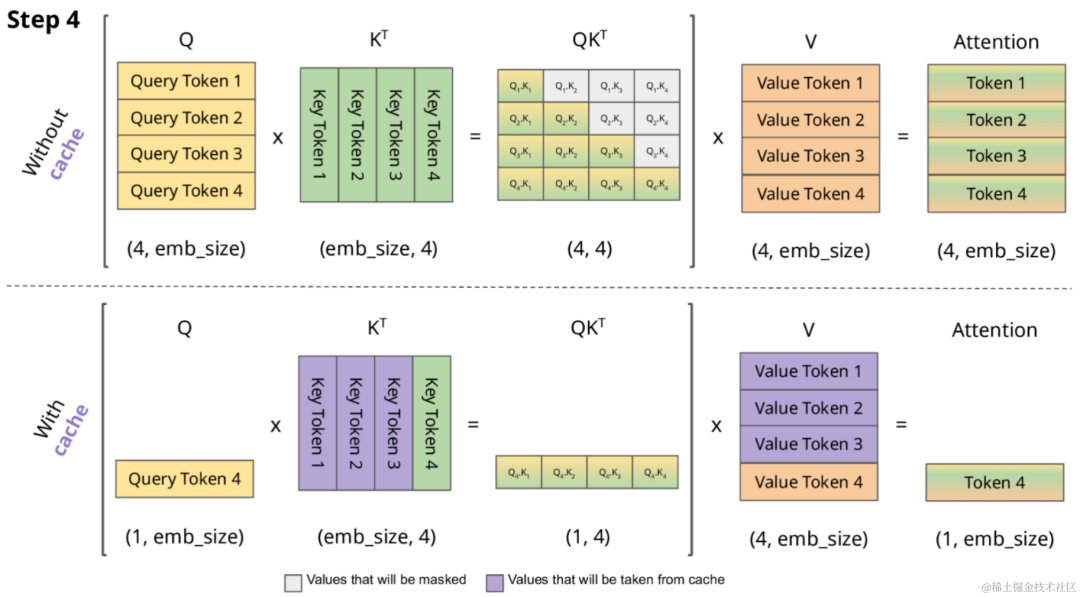
使不使用 KV Cache 的对比
下图展示了使用KV Cache和不使用KV Cache的对比,其中,紫色部分表示从缓存获取,灰色部分表示会被Masked。



下面使用 transformers 来比较有 KV Cache 和没有 KV Cache的情况下,GPT-2的生成速度。
importnumpyasnp
importtime
importtorch
fromtransformersimportAutoModelForCausalLM,AutoTokenizer
device="cuda"iftorch.cuda.is_available()else"cpu"
tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
model=AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2").to(device)
foruse_cachein(True,False):
times=[]
for_inrange(10):#measuring10generations
start=time.time()
model.generate(**tokenizer("WhatisKVcaching?",return_tensors="pt").to(device),use_cache=use_cache,max_new_tokens=1000)
times.append(time.time()-start)
print(f"{'with'ifuse_cacheelse'without'}KVcaching:{round(np.mean(times),3)}+-{round(np.std(times),3)}seconds")
运行结果:
- 使用 KV caching: 11.885 +- 0.272 秒
- 不使用 KV caching: 56.197 +- 1.855 秒
可以看到使不使用 KV cache 推理性能果差异显存。
使用 KV Cache 解码阶段计算量分析
FLOPs,floating point operations,表示浮点数运算次数,衡量了计算量的大小。
如何计算矩阵乘法的FLOPs呢?
对于,计算??需要进行?次乘法运算和?次加法运算,共计2?次浮点数运算,需要的FLOPs。对于,计算??需要的浮点数运算次数为。
下面来看看在一个 Token 生成过程中一层 Transformer 的计算量。
首先,分析 self-attention 块的计算,计算公式如下:
我们来看看不使用 KV Cache 时,假设输入数据的形状为[b, s],隐藏层维度为 h,则输入的形状为 [b, s, h]。self-attention块的计算如下:
- 计算?,?,?:矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,?,ℎ]×[ℎ,ℎ]→[?,?,ℎ]。计算量为$ 3* bs2hh = 3∗2??ℎ^2=6??ℎ^2$。 - 矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,ℎ???_???, ?, ???_ℎ???_ℎ?????_????]×[?, ℎ???_???, ???_ℎ???_ℎ?????_????, ?]→[?, ℎ???_???, ?, ?],计算量为。 - 计算在?上的加权?????⋅?,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,ℎ???_???,?,?]×[?,ℎ???_???,?,???_ℎ???_ℎ?????_????]→[?,ℎ???_???,?,???_ℎ???_ℎ?????_????]。计算量为。 - attention后的线性映射,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,?,ℎ]×[ℎ,ℎ]→[?,?,ℎ]。计算量为。
不使用 KV Cache 时,输入的形状为 [b, 1, h ],kv cache中含有 个 past word。self-attention块的计算如下:
- 矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[b, head_num, 1, per_head_hidden_size]×[b, head_num, per_head_hidden_size, kv_length+1]→[b, head_num, 1, kv_length+1] 。计算量为。 - 计算在?上的加权?????·?,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[b, head_num, 1, kv_length+1]×[b,head_num,kv_length+1,per_head_hidden_size]→[b,head_num,1,per_head_hidden_size] 。计算量为。 - attention后的线性映射,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,1,ℎ]×[ℎ,ℎ]→[?,1,ℎ]。计算量为。
接下来分析MLP块的计算,计算公式如下:
不使用 KV Cache 时:
- 第一个线性层,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,?,ℎ]×[ℎ,4ℎ]→[?,?,4ℎ]。计算量为。 - 第二个线性层,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,?,4ℎ]×[4ℎ,ℎ]→[?,?,ℎ]。计算量为。
使用 KV Cache 时:
- 第一个线性层,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?, 1, ℎ]×[ℎ, 4ℎ]→[?,1,4ℎ]。计算量为。 - 第二个线性层,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?, 1, 4ℎ]×[4ℎ, ℎ]→[?,1,ℎ]。计算量为。
将上述self-attention块和MLP块计算量相加,得到:
- 不采用kv cache时,得到每个transformer层的计算量大约为: 。
此外,另一个计算量的大头是logits的计算,将隐藏向量映射为词表大小。
- 采用kv cache时,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,1,ℎ]×[ℎ,?]→[?,1,?],计算量为。 - 不采用kv cache时为,矩阵乘法的输入和输出形状为
[?,?,ℎ]×[ℎ,?]→[?,?,?],计算量为。
KV Cache 显存占用分析
假设输入序列的长度为s,输出序列的长度为n ,transformer层数为l,隐藏层维度 h,KV Cache 存储 kv_seq_len 个 KV value,形状为 [b, head_num, kv_seq_len, head_dim], 峰值kv_seq_len为 s+n ,以float16来保存KV cache,那么KV cache的峰值显存占用大小为b(s+n)hl2*2=4blh(s+n)。这里第一个 2 表示 K/V cache,第二个2表示float16占 2 个 bytes。
以GPT3-175B为例,对比KV cache与模型参数占用显存的大小。模型配置如下:
| 模型名 | 参数量 | 层数 | 隐藏维度 | 注意力头数 |
|---|
| GPT3 | 175B | 96 | 12288 | 96 |
GPT3 模型占用显存大小为350GB。假设批次大小b=64,输入序列长度s=512,输出序列长度n=32,则KV cache 峰值占用显存为4blh(s+n) = 164,282,499,072 bytes ≈ 164 ??,大约是模型参数显存的0.5倍。
KV Cache 存在的问题以及优化措施
当将LLMs应用于无限输入流时,使用原始的 Dense Attention 会出现两个主要挑战:
- 上下文越长,那么矩阵占用的内存也会越多,不仅如此还会增加Decoder时候的延迟。
- 现有模型的长度外推能力有限,即当序列长度超出预训练期间设置的attention窗口大小时,其性能会下降。
因此,目前提出了一些优化方法,比如:使用滑动窗口的注意力机制,主要有如下几种方式。
- 一种方式是如下图 B 的窗口注意力(Window Attention):只缓存最近的 L 个 Token 的 KV。虽然推理效率很高,但一旦起始Token的键和值被驱逐,性能就会急剧下降。
- 一种方式是下图 C 的滑动窗口重计算(Sliding Window w/ Re-computation):根据每个新 Token 的 L 个最近 Token 重建 KV 状态。虽然它在长文本上表现良好,但其 的复杂性(源于上下文重新计算中的二次注意力)使其相当慢。

- 还有一种方式是StreamingLLM,在当前滑动窗口方法的基础上,重新引入了一些最初的 tokens 的KV在注意力计算中使用。StreamingLLM 中的KV缓存可以概念上分为两部分,如下图所示:(1)attention sink 是 4 个最初的 tokens,稳定了注意力计算;(2)Rolling KV Cache 保留了最近的token,这个窗口值是固定的。此外,还需要有些小改动来给attention注入位置信息,StreamingLLM就可以无缝地融入任何使用相对位置编码的自回归语言模型,如RoPE和ALiBi。

KV Cache 源码分析
GPT2 中 KV Cache 代码实现:
classGPT2Attention(nn.Module):
defforward(
self,
hidden_states:Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]],
layer_past:Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]=None,
attention_mask:Optional[torch.FloatTensor]=None,
head_mask:Optional[torch.FloatTensor]=None,
encoder_hidden_states:Optional[torch.Tensor]=None,
encoder_attention_mask:Optional[torch.FloatTensor]=None,
use_cache:Optional[bool]=False,
output_attentions:Optional[bool]=False,
)->Tuple[Union[torch.Tensor,Tuple[torch.Tensor]],...]:
...
#拆分Q、K、V
query,key,value=self.c_attn(hidden_states).split(self.split_size,dim=2)
...
#[batch,sequence_len,embeded_dim]->[batch,heads,sequence_len,head_dim]
query=self._split_heads(query,self.num_heads,self.head_dim)#当前token对应的query
key=self._split_heads(key,self.num_heads,self.head_dim)#当前token对应的key
value=self._split_heads(value,self.num_heads,self.head_dim)#当前token对应的value
##################################
#KVCache核心代码逻辑
iflayer_pastisnotNone:
past_key,past_value=layer_past#从KVCache去数据
key=torch.cat((past_key,key),dim=-2)#将当前token的key与历史的K拼接
value=torch.cat((past_value,value),dim=-2)#将当前token的value与历史的V拼接
ifuse_cacheisTrue:
present=(key,value)#将数据存到KVCache
else:
present=None
##################################
...
#使用当前token的query与K和V计算注意力表示
attn_output,attn_weights=self._attn(query,key,value,attention_mask,head_mask)#返回att输出(激活)和权重
#合并多头注意力
#attn_output:[batch,heads,sequence_len,head_dim]->[batch,heads,embed_dim]
attn_output=self._merge_heads(attn_output,self.num_heads,self.head_dim)
attn_output=self.c_proj(attn_output)
attn_output=self.resid_dropout(attn_output)
outputs=(attn_output,present)
ifoutput_attentions:
outputs+=(attn_weights,)
returnoutputs#a,present,(attentions)
Baichuan2 中 KV Cache 代码实现:
classAttention(nn.Module):
defforward(
self,
hidden_states:torch.Tensor,
attention_mask:Optional[torch.Tensor]=None,
position_ids:Optional[torch.LongTensor]=None,
past_key_value:Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]=None,
output_attentions:bool=False,
use_cache:bool=False,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,Optional[torch.Tensor],Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
bsz,q_len,_=hidden_states.size()
proj=self.W_pack(hidden_states)
proj=proj.unflatten(-1,(3,self.hidden_size)).unsqueeze(0).transpose(0,-2).squeeze(-2)
query_states=proj[0].view(bsz,q_len,self.num_heads,self.head_dim).transpose(1,2)
key_states=proj[1].view(bsz,q_len,self.num_heads,self.head_dim).transpose(1,2)
value_states=proj[2].view(bsz,q_len,self.num_heads,self.head_dim).transpose(1,2)
kv_seq_len=key_states.shape[-2]
ifpast_key_valueisnotNone:
kv_seq_len+=past_key_value[0].shape[-2]
cos,sin=self.rotary_emb(value_states,seq_len=kv_seq_len)
query_states,key_states=apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states,key_states,cos,sin,position_ids)
#[bsz,nh,t,hd]
ifpast_key_valueisnotNone:
#取出KVCache中的值
#reusek,v,self_attention
key_states=torch.cat([past_key_value[0],key_states],dim=2)
value_states=torch.cat([past_key_value[1],value_states],dim=2)
#保存KVCache中的值
past_key_value=(key_states,value_states)ifuse_cacheelseNone
Huggingface Transformer 库中 LLaMA 中 KV Cache 代码实现:
classLlamaAttention(nn.Module):
...
defforward(
self,
hidden_states:torch.Tensor,
attention_mask:Optional[torch.Tensor]=None,
position_ids:Optional[torch.LongTensor]=None,
past_key_value:Optional[Cache]=None,
output_attentions:bool=False,
use_cache:bool=False,
cache_position:Optional[torch.LongTensor]=None,
**kwargs,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,Optional[torch.Tensor],Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
...
past_key_value=getattr(self,"past_key_value",past_key_value)
cos,sin=self.rotary_emb(value_states,position_ids)
query_states,key_states=apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states,key_states,cos,sin)
ifpast_key_valueisnotNone:
#sinandcosarespecifictoRoPEmodels;cache_positionneededforthestaticcache
cache_kwargs={"sin":sin,"cos":cos,"cache_position":cache_position}
#将当前Token的kv值更新到KVCache,并返回新的KV
key_states,value_states=past_key_value.update(key_states,value_states,self.layer_idx,cache_kwargs)
...
returnattn_output,attn_weights,past_key_value
Huggingface Transformer 库中对Cache进行了抽象,里面实现了各种Cache,如:生成模型默认的动态缓存DynamicCache、StaticCache 和 StreamingLLM 论文中提到的SinkCache。
@dataclass
classCache:
"""
所有Cache的基础抽象类。实际数据结构由每个子类决定。
"""
defupdate(
self,
key_states:torch.Tensor,
value_states:torch.Tensor,
layer_idx:int,
cache_kwargs:Optional[Dict[str,Any]]=None,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,torch.Tensor]:
"""
Updatesthecachewiththenew`key_states`and`value_states`forthelayer`layer_idx`.
Parameters:
key_states(`torch.Tensor`):
Thenewkeystatestocache.
value_states(`torch.Tensor`):
Thenewvaluestatestocache.
layer_idx(`int`):
Theindexofthelayertocachethestatesfor.
cache_kwargs(`Dict[str,Any]`,`optional`):
Additionalargumentsforthecachesubclass.Thesearespecifictoeachsubclassandallownewtypesof
cachetobecreated.
Return:
Atuplecontainingtheupdatedkeyandvaluestates.
"""
raiseNotImplementedError("Makesuretoimplement`update`inasubclass.")
defget_seq_length(self,layer_idx:Optional[int]=0)->int:
"""Returnsthesequencelengthofthecachedstates.Alayerindexcanbeoptionallypassed."""
raiseNotImplementedError("Makesuretoimplement`get_seq_length`inasubclass.")
defget_max_length(self)->Optional[int]:
"""Returnsthemaximumsequencelengthofthecachedstates,ifthereisany."""
raiseNotImplementedError("Makesuretoimplement`get_max_length`inasubclass.")
defget_usable_length(self,new_seq_length:int,layer_idx:Optional[int]=0)->int:
"""Giventhesequencelengthofthenewinputs,returnstheusablelengthofthecache."""
#Cachewithoutsizelimit->allcacheisusable
#Cachewithsizelimit->ifthelengthcacheplusthelengthofthenewinputsislargerthemaximumcache
#length,wewillneedtoevictpartofthecache(andthusnotallcacheisusable)
max_length=self.get_max_length()
previous_seq_length=self.get_seq_length(layer_idx)
ifmax_lengthisnotNoneandprevious_seq_length+new_seq_length>max_length:
returnmax_length-new_seq_length
returnprevious_seq_length
@property
defseen_tokens(self):
logger.warning_once(
"The`seen_tokens`attributeisdeprecatedandwillberemovedinv4.41.Usethe`cache_position`"
"modelinputinstead."
)
ifhasattr(self,"_seen_tokens"):
returnself._seen_tokens
else:
returnNone
classDynamicCache(Cache):
#随着生成更多Token而动态增长的Cache。这是生成模型的默认设置。
#它将键和值状态存储为张量列表,每层一个张量。每个张量的期望形状是
#[batch_size,num_heads,seq_len,head_dim]。
defupdate(
self,
key_states:torch.Tensor,
value_states:torch.Tensor,
layer_idx:int,
cache_kwargs:Optional[Dict[str,Any]]=None,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,torch.Tensor]:
#Updatethenumberofseentokens
iflayer_idx==0:
self._seen_tokens+=key_states.shape[-2]
#Updatethecache
iflen(self.key_cache)<=layer_idx:
self.key_cache.append(key_states)
self.value_cache.append(value_states)
else:
self.key_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([self.key_cache[layer_idx],key_states],dim=-2)
self.value_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([self.value_cache[layer_idx],value_states],dim=-2)
returnself.key_cache[layer_idx],self.value_cache[layer_idx]
classStaticCache(Cache):
"""
与torch.compile(model)一起使用的静态Cache类
"""
...
defupdate(
self,
key_states:torch.Tensor,
value_states:torch.Tensor,
layer_idx:int,
cache_kwargs:Optional[Dict[str,Any]]=None,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,torch.Tensor]:
"""
Updatesthecachewiththenew`key_states`and`value_states`forthelayer`layer_idx`.
使用张量进行索引是非常重要的,否则你会向设备引入一个副本。
Parameters:
key_states(`torch.Tensor`):
Thenewkeystatestocache.
value_states(`torch.Tensor`):
Thenewvaluestatestocache.
layer_idx(`int`):
Theindexofthelayertocachethestatesfor.Keptforbackwardcompatibility
cache_kwargs(`Dict[str,Any]`,`optional`):
Additionalargumentsforthecachesubclass.The`StaticCache`justneedsthe`q_len`
toknowhowmuchofthecacheitshouldoverwrite.
Return:
Atuplecontainingtheupdatedkeyandvaluestates.
"""
new_cache_positions=cache_kwargs.get("cache_position")
k_out=self.key_cache
v_out=self.value_cache
k_out[:,:,new_cache_positions]=key_states
v_out[:,:,new_cache_positions]=value_states
returnk_out,v_out
classSinkCache(Cache):
"""
#正如[AttentionSinks论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.17453)中所描述的缓存。
#它允许模型生成超出其上下文窗口的长度,而不会失去会话的流畅性。
#因为它抛弃了过去tokens,模型将失去生成依赖于被丢弃的上下文的tokens的能力。
#它将键和值状态存储为张量列表,每层一个张量。每个张量的期望形状是
#[batch_size,num_heads,seq_len,head_dim]
"""
...
defupdate(
self,
key_states:torch.Tensor,
value_states:torch.Tensor,
layer_idx:int,
cache_kwargs:Optional[Dict[str,Any]]=None,
)->Tuple[torch.Tensor,torch.Tensor]:
#Optionalkwargsfor`SinkCache`--neededonmodelsusingRoPE.`partial_rotation_size`isusedonmodels
#withpartiallyrotatedpositionembeddings,likePhiorPersimmon.
sin=cache_kwargs.get("sin")
cos=cache_kwargs.get("cos")
partial_rotation_size=cache_kwargs.get("partial_rotation_size")
using_rope=cosisnotNoneandsinisnotNone
#Updatethenumberofseentokens
iflayer_idx==0:
self._seen_tokens+=key_states.shape[-2]
#[bsz,num_heads,seq_len,head_dim]
iflen(self.key_cache)<=layer_idx:
#Emptycache
self.key_cache.append(key_states)
self.value_cache.append(value_states)
elifkey_states.shape[-2]+self.get_seq_length(layer_idx)<self.window_length:
#Growingcache
self.key_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([self.key_cache[layer_idx],key_states],dim=-2)
self.value_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([self.value_cache[layer_idx],value_states],dim=-2)
else:
#Shiftingcache
keys_to_keep=self.key_cache[layer_idx][
:,:,-self.window_length+self.num_sink_tokens+key_states.shape[-2]:
]
#OnRoPEmodels,weneedtorecomputetheKeyrotationasthetokensareshifted
ifusing_rope:
rerotation_cos,rerotation_sin=self._get_rerotation_cos_sin(
key_states,cos[:self.window_length],sin[:self.window_length]
)
ifpartial_rotation_sizeisnotNone:
keys_to_keep,keys_pass=(
keys_to_keep[...,:partial_rotation_size],
keys_to_keep[...,partial_rotation_size:],
)
keys_to_keep=self._apply_key_rotary_pos_emb(keys_to_keep,rerotation_cos,rerotation_sin)
ifpartial_rotation_sizeisnotNone:
keys_to_keep=torch.cat((keys_to_keep,keys_pass),dim=-1)
#Concatenatesinktokens,shifted&rotatedtokens(ifneeded),andnewtokens
sink_keys=self.key_cache[layer_idx][:,:,:self.num_sink_tokens]
self.key_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([sink_keys,keys_to_keep,key_states],dim=-2)
sink_values=self.value_cache[layer_idx][:,:,:self.num_sink_tokens]
values_to_keep=self.value_cache[layer_idx][
:,:,-self.window_length+self.num_sink_tokens+value_states.shape[-2]:
]
self.value_cache[layer_idx]=torch.cat([sink_values,values_to_keep,value_states],dim=-2)
returnself.key_cache[layer_idx],self.value_cache[layer_idx]
从 GPT2 、 Baichuan2 和 LLaMA 的源码中可以看到 KV Cache 核心代码的实现就几行并不复杂,但是带来的收益却挺大。
结语
本文简要分析了 KV Cache 原理、源码以及计算量和显存占用,这是一种典型的通过空间换时间(计算)的技术,虽然并不复杂,但是现在基本上是仅编码器Transformer架构生成大语言模型必备优化技术。