别再被MCP协议绕晕!一文搞懂连接流程与核心架构
? 文章目标
本文面向AI 应用开发者以及对模型上下文协议感兴趣的技术人员,旨在帮助大家:
- 理解MCP协议的核心原理:掌握客户端-服务器架构设计和通信机制的本质。
- 深入学习传输层实现:详细了解Stdio传输机制、JSON-RPC 2.0协议的工作原理和实际应用。
- 掌握关键技术实现:包括进程间通信、消息序列化、错误处理以及如何构建稳定的MCP连接。
- 学会实际应用开发:从理论到实践,能够独立开发和调试MCP服务器和客户端程序。
? 小提示
本文基于官方MCP文档规范编写,所有示例代码均经过实际测试验证。文末提供完整的可运行代码示例。本次文档代码可以在https://github.com/li-xiu-qi/XiaokeAILabs/tree/main/datas/test_Agent/test_mcp/mcp_theory找到更多代码示例
? 目录
- ? JSON-RPC 1.0 vs 2.0 核心差异
? 前言
最近有很多朋友问我:MCP协议到底是什么?为什么大家都在说它很重要?
确实,Model Context Protocol (MCP) 作为Anthropic推出的开放标准,正在成为AI应用生态的重要基础设施。但很多技术文章要么过于理论化,要么缺乏实际操作指导,让初学者摸不着头脑。
本文将通过图解+代码+实战的方式,带你彻底搞懂MCP协议的核心机制。我们会从最基础的概念开始,逐步深入到技术实现细节,最后通过完整的代码示例让你能够亲手搭建一个MCP系统。
为什么要学习MCP?
- 标准化的AI工具连接- 让你的AI应用能够标准化地访问各种外部工具和数据源
- 简化集成复杂度- 统一的协议规范大幅降低了不同系统间的集成成本
- 企业级应用前景- 各大厂商都在积极支持,是AI应用开发的未来趋势
如果你正在开发AI应用,或者想要了解现代AI系统的底层通信机制,这篇文章绝对值得仔细阅读!
觉得有收获记得给我点赞、关注,转发给需要的人,作者的创作能量就差您这关键的一份鼓励,您的支持必不可少!
好了,让我们开始这场MCP协议的探索之旅吧!
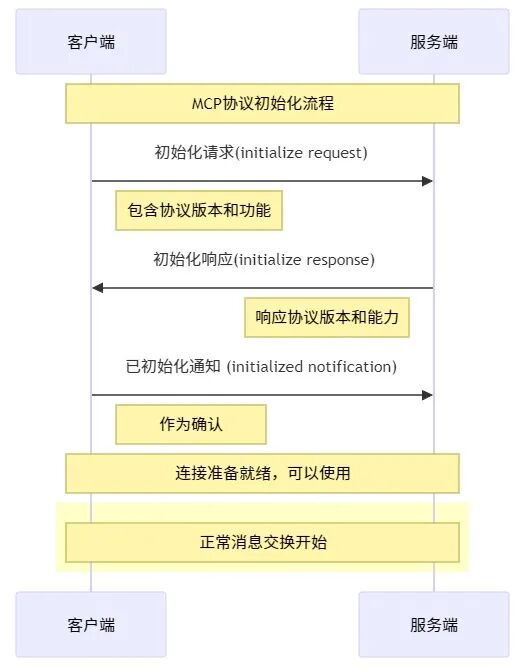
? MCP连接流程概览
让我们先从最直观的连接时序图开始理解MCP的工作流程:

? 连接流程说明
整个MCP连接过程包含四个关键步骤:
- 客户端发送初始化请求- 包含协议版本和客户端功能声明
- 服务器响应其协议版本和能力- 告知客户端服务器支持的功能
- 客户端发送已初始化通知作为确认- 确认初始化完成,可以开始正常通信
这个看似简单的握手过程,实际上解决了版本兼容性、能力协商等复杂问题。就像TCP三次握手一样,确保了双方能够可靠通信。
?️ MCP协议核心架构详解
参考资料: MCP官方架构文档:地址:https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-03-26/architecture
架构概述
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 采用经典的客户端-服务器架构设计,这种设计让大型语言模型(LLM)应用程序能够与各种集成服务进行标准化通信。
? 架构角色解析

在MCP体系中,有三个核心角色:
- ? 宿主(Host):LLM应用程序的载体,比如Claude Desktop、VS Code等IDE,负责发起连接并管理整个交互流程
- ? 客户端(Client):运行在宿主应用程序内部的组件,与服务器保持一对一连接,处理具体的通信逻辑
- ? 服务器(Server):为客户端提供上下文、工具和提示服务的后端程序,是功能的实际提供者
这种分层设计的优势在于:职责清晰、可扩展性强、便于维护。
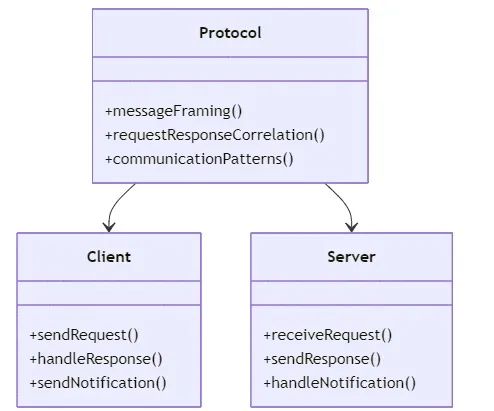
? 核心组件架构
MCP协议栈分为两个主要层次:
1. 协议层(Protocol Layer)
协议层在MCP负责:
- 高级通信模式- 支持同步、异步、通知等多种通信方式
2. 传输层(Transport Layer)
传输层在MCP负责实际的数据传输:
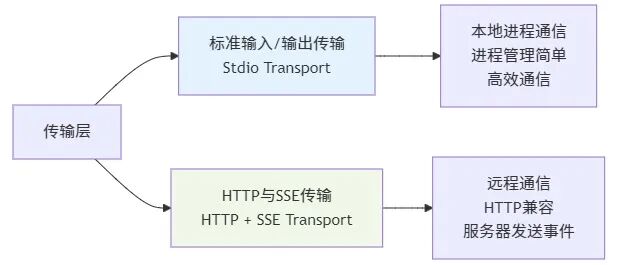
MCP支持多种传输机制,目前主要包括:
- HTTP + SSE传输- 基于HTTP协议的网络通信
? Stdio传输深度解析
参考资料: MCP传输层官方文档,地址:https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/concepts/transports | Python subprocess模块文档,地址:https://docs.python.org/3/library/subprocess.html
? 什么是Stdio?
Stdio(Standard Input/Output,标准输入输出)是操作系统提供的基础I/O机制。每个进程启动时都会自动获得三个标准文件描述符,这是程序与外界交互的基本通道。
? Stdio的本质理解
Stdio本质上就是捕获和重定向终端输入输出。让我们通过对比来深入理解:

? 传统终端交互 vs MCP Stdio传输
1. 传统终端交互模式:
# 用户在终端中手动运行程序
C:\> python my_server.py
# 用户手动输入JSON消息
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"test","id":1}
# 程序输出响应到屏幕
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","result":"success","id":1}
2. MCP Stdio传输模式:
# 客户端程序自动启动服务器并捕获I/O
importsubprocess
# 启动服务器进程,捕获其stdin/stdout
process = subprocess.Popen(
['python','my_server.py'],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE, # 捕获服务器的输入
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, # 捕获服务器的输出
stderr=subprocess.PIPE, # 捕获服务器的错误输出
text=True
)
# 客户端发送数据到服务器的stdin(模拟用户在终端输入)
process.stdin.write('{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"test","id":1}\n')
process.stdin.flush()
# 客户端读取服务器的stdout(捕获程序的终端输出)
response = process.stdout.readline()
print(f"服务器响应:{response}")
? Stdio的三个标准流详解

?️ 实际代码示例
让我们通过一个完整的例子来理解Stdio在MCP中的应用:
服务器端实现
importsys
importjson
defmain():
"""MCP服务器主函数"""
whileTrue:
try:
# 从stdin读取客户端消息(相当于等待终端输入)
line = sys.stdin.readline()
ifnotline:
break
# 解析JSON-RPC请求
request = json.loads(line.strip())
# 处理请求并生成响应
ifrequest.get('method') =='echo':
response = {
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"result":f"Echo:{request.get('params','')}",
"id": request.get('id')
}
else:
response = {
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"error": {"code":-32601,"message":"Method not found"},
"id": request.get('id')
}
# 向stdout输出响应(相当于终端输出)
print(json.dumps(response), flush=True)
exceptExceptionase:
# 错误信息发送到stderr(终端错误输出)
print(f"Error:{e}", file=sys.stderr, flush=True)
if__name__ =="__main__":
main()
客户端实现
importsubprocess
importjson
classMCPStdioClient:
"""MCP Stdio客户端封装"""
def__init__(self):
# 启动服务器进程,捕获其所有I/O流
self.process = subprocess.Popen(
['python','my_mcp_server.py'],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE, # 我们控制服务器的输入
stdout=subprocess.PIPE, # 我们捕获服务器的输出
stderr=subprocess.PIPE, # 我们捕获服务器的错误
text=True,
bufsize=0# 无缓冲,实时通信
)
defsend_request(self, method, params=None):
"""发送请求到MCP服务器"""
# 构造JSON-RPC请求
request = {
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"method": method,
"params": params,
"id":1
}
# 发送到服务器的stdin(模拟在终端输入)
json_str = json.dumps(request) +'\n'
self.process.stdin.write(json_str)
self.process.stdin.flush()
# 从服务器的stdout读取响应(捕获终端输出)
response_line = self.process.stdout.readline()
returnjson.loads(response_line.strip())
defclose(self):
"""关闭连接"""
self.process.terminate()
self.process.wait()
# 使用示例
client = MCPStdioClient()
# 发送测试请求
response = client.send_request("echo","Hello MCP!")
print(f"服务器响应:{response}")
# 输出: 服务器响应: {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": "Echo: Hello MCP!", "id": 1}
client.close()
⚡ Stdio传输的技术优势
相比网络传输方式,Stdio传输有以下显著优势:
? MCP Stdio传输工作时序
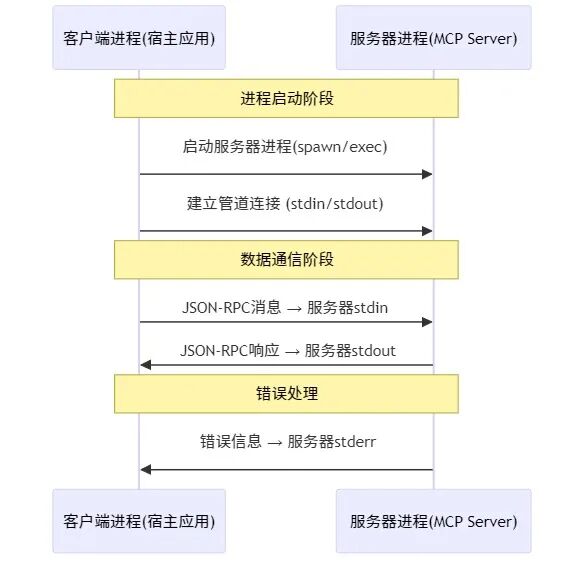
? 跨平台实现差异
Python的subprocess模块为我们屏蔽了这些平台差异,提供了统一的编程接口。
? 传输方式选择指南
| | | |
|---|
| Stdio 传输 | 本地应用集成 | | |
| HTTP + SSE 传输 | 分布式系统 | | |
? JSON-RPC 2.0协议详解
参考资料: JSON-RPC 2.0官方规范,地址:https://www.jsonrpc.org/specification
? 什么是JSON-RPC?
JSON-RPC是一个基于JSON格式的远程过程调用(Remote Procedure Call, RPC)协议规范。它让客户端能够通过网络调用远程服务器上的方法,就像调用本地函数一样简单。
? JSON-RPC版本演进历史

? JSON-RPC 1.0 vs 2.0 核心差异
1. 协议版本标识
// JSON-RPC 1.0 - 没有版本字段
{
"method":"echo",
"params": ["Hello"],
"id":1
}
// JSON-RPC 2.0 - 必须包含版本字段
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"method":"echo",
"params": ["Hello"],
"id":1
}
2. 参数传递方式增强
| | |
|---|
| 参数类型 | | |
| 位置参数 | | |
| 命名参数 | | ✓{"name": "value", "age": 30} |
3. 功能特性对比表
? MCP中的JSON-RPC 2.0消息格式
1. 请求消息格式
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0", // 协议版本,必须是"2.0"
"method":"initialize", // 要调用的方法名
"params": { // 参数对象(可选)
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {...}
},
"id":1 // 请求标识符
}
2. 成功响应格式
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0", // 协议版本
"result": { // 方法执行结果
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {...}
},
"id":1 // 与请求对应的ID
}
3. 错误响应格式
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0", // 协议版本
"error": { // 错误对象
"code":-32602, // 错误代码
"message":"Invalid params",// 错误描述
"data": { // 额外错误信息(可选)
"details":"Missing required parameter 'name'"
}
},
"id":1 // 与请求对应的ID
}
4. 通知消息格式
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0", // 协议版本
"method":"notifications/initialized",// 方法名
"params": {...} // 参数(可选)
// 注意:通知消息没有id字段,因此不需要响应
}
❌ JSON-RPC 2.0错误代码规范
? 批处理支持
JSON-RPC 2.0支持批处理,可以在一次传输中发送多个请求:
// 批处理请求
[
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"prompts/list","id":1},
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"tools/list","id":2},
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"resources/list","id":3}
]
// 批处理响应
[
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","result": [...],"id":1},
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","result": [...],"id":2},
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","result": [...],"id":3}
]
? 连接生命周期详解
? 完整生命周期流程

初始化阶段详细步骤
Step 1: 客户端发送初始化请求
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"initialize",
"params": {
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {
"roots": {
"listChanged":true
},
"sampling": {}
},
"clientInfo": {
"name":"ExampleClient",
"version":"1.0.0"
}
}
}
Step 2: 服务器响应初始化
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"result": {
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {
"logging": {},
"prompts": {
"listChanged":true
},
"resources": {
"subscribe":true,
"listChanged":true
},
"tools": {
"listChanged":true
}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name":"ExampleServer",
"version":"1.0.0"
},
"instructions":"Optional instructions for the client"
}
}
Step 3: 客户端发送已初始化通知
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"method":"notifications/initialized"
}
消息交换模式
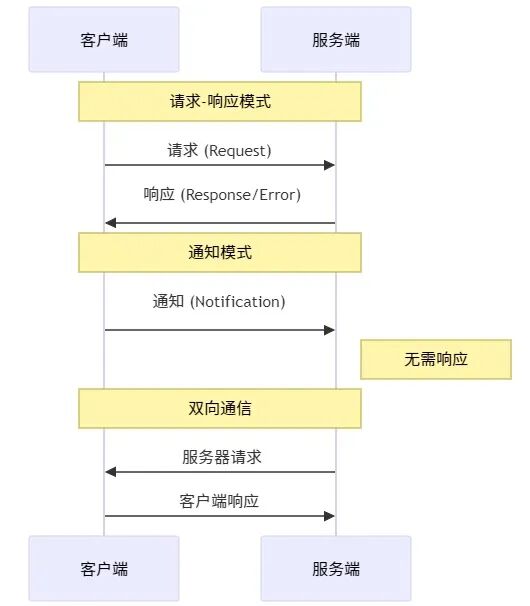
MCP支持三种主要的消息交换模式:
终止处理

优雅的连接终止包括:
⚠️ 错误处理机制
参考资料: JSON-RPC 2.0错误处理规范,地址:https://www.jsonrpc.org/specification#error_object
标准错误代码体系
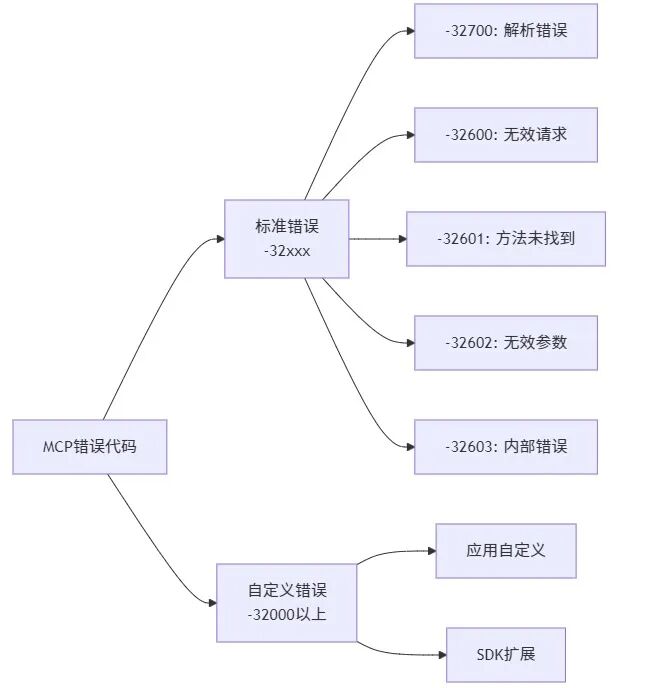
? 错误传播机制
// 错误响应示例
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"error": {
"code":-32602,
"message":"Invalid params",
"data": {
"details":"Required parameter 'name' is missing"
}
}
}
?️ 实现最佳实践
? 传输选择策略
? 消息处理最佳实践
1. 请求处理模板
asyncdefhandle_request(request):
"""标准的MCP请求处理流程"""
try:
# 1. 验证输入
validate_input(request.params)
# 2. 类型安全处理
result =awaitprocess_request_safely(request)
# 3. 返回结果
return{"result": result}
exceptValidationErrorase:
return{"error": {"code":-32602,"message": str(e)}}
exceptTimeoutError:
return{"error": {"code":-32603,"message":"Request timeout"}}
exceptExceptionase:
return{"error": {"code":-32603,"message":f"Internal error:{str(e)}"}}
2. 进度报告机制
asyncdeflong_operation(progress_token):
"""长时间操作的进度报告示例"""
total_steps =100
foriinrange(total_steps):
# 执行操作
awaitperform_step(i)
# 报告进度
ifprogress_token:
awaitsend_progress({
"token": progress_token,
"value": i +1,
"total": total_steps
})
? 安全考虑
参考资料: MCP安全与信任指南,地址:https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-03-26#security-and-trust--safety
多层安全架构

✅ 安全检查清单
| | |
|---|
| 传输安全 | • 远程连接使用TLS
• 验证连接来源
• 实现适当的身份验证 | |
| 消息安全 | • 验证所有传入消息
• 清理和转义输入
• 检查消息大小限制 | |
| 资源安全 | | |
? 调试与监控
? 关键监控指标

重要的监控指标包括:
? 结构化日志实现
importlogging
importjson
importtime
classMCPLogger:
"""MCP协议专用日志记录器"""
def__init__(self):
self.logger = logging.getLogger('mcp')
deflog_protocol_event(self, event_type, details):
"""记录协议事件"""
self.logger.info(json.dumps({
"type":"protocol_event",
"event": event_type,
"timestamp": time.time(),
"details": details
}))
deflog_message_flow(self, direction, message):
"""记录消息流"""
self.logger.debug(json.dumps({
"type":"message_flow",
"direction": direction, # "incoming" or "outgoing"
"message_id": message.get("id"),
"method": message.get("method"),
"timestamp": time.time()
}))
? 快速开始实战
想要快速体验MCP协议的魅力吗?跟着下面的步骤,15分钟就能搭建一个完整的MCP系统!
1. 环境准备
# 创建项目目录
mkdir mcp-tutorial &&cdmcp-tutorial
# 安装依赖(Python 3.7+)
pip install asyncio
? 2. 创建MCP服务器
创建mcp_server.py:
importsys
importjson
importasyncio
classSimpleMCPServer:
"""简单的MCP服务器实现"""
def__init__(self):
self.running =True
print("? MCP服务器启动中...", file=sys.stderr)
print("? 等待客户端连接...", file=sys.stderr)
asyncdefhandle_message(self, message):
"""处理客户端消息"""
print(f"? 收到消息:{message}", file=sys.stderr)
# 验证JSON-RPC格式
ifnotisinstance(message, dict):
returnself.create_error_response(None,-32600,"Invalid Request")
ifmessage.get('jsonrpc') !='2.0':
returnself.create_error_response(message.get('id'),-32600,"Invalid JSON-RPC version")
method = message.get('method')
ifnotmethod:
returnself.create_error_response(message.get('id'),-32600,"Missing method")
# 处理不同的方法
ifmethod =='initialize':
return{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id": message['id'],
"result": {
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {},
"resources": {},
"prompts": {}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name":"SimpleMCPServer",
"version":"1.0.0"
}
}
}
elifmethod =='ping':
return{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id": message['id'],
"result": {"message":"pong","timestamp": __import__('time').time()}
}
else:
returnself.create_error_response(message.get('id'),-32601,f"Method not found:{method}")
defcreate_error_response(self, request_id, code, message):
"""创建错误响应"""
return{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id": request_id,
"error": {"code": code,"message": message}
}
asyncdefrun(self):
"""服务器主循环"""
whileself.running:
try:
# 从stdin读取消息
line =awaitasyncio.get_event_loop().run_in_executor(
None, sys.stdin.readline
)
ifnotline:
print("? 客户端断开连接", file=sys.stderr)
break
line = line.strip()
ifnotline:
continue
# 解析JSON消息
try:
message = json.loads(line)
exceptjson.JSONDecodeErrorase:
error_response = self.create_error_response(None,-32700,f" arse error:{str(e)}")
arse error:{str(e)}")
print(json.dumps(error_response), flush=True)
continue
# 处理消息
response =awaitself.handle_message(message)
# 发送响应
ifresponse:
response_json = json.dumps(response)
print(f"? 发送响应:{response_json}", file=sys.stderr)
print(response_json, flush=True)
exceptExceptionase:
print(f"? 服务器错误:{e}", file=sys.stderr)
error_response = self.create_error_response(None,-32603,f"Internal error:{str(e)}")
print(json.dumps(error_response), flush=True)
if__name__ =="__main__":
server = SimpleMCPServer()
asyncio.run(server.run())
3. 创建MCP客户端
创建mcp_client.py:
importsubprocess
importjson
importtime
classSimpleMCPClient:
"""简单的MCP客户端实现"""
def__init__(self):
print("? 启动MCP客户端...")
# 启动服务器进程
self.process = subprocess.Popen(
['python','mcp_server.py'],
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True
)
self.request_id =0
print("✅ 服务器进程已启动")
defsend_request(self, method, params=None):
"""发送请求到服务器"""
self.request_id +=1
request = {
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id": self.request_id,
"method": method
}
ifparams:
request["params"] = params
# 发送请求
request_json = json.dumps(request) +'\n'
print(f"? 发送请求:{request}")
self.process.stdin.write(request_json)
self.process.stdin.flush()
# 读取响应
response_line = self.process.stdout.readline()
response = json.loads(response_line.strip())
print(f"? 收到响应:{response}")
returnresponse
defclose(self):
"""关闭客户端"""
print("? 关闭连接...")
self.process.terminate()
self.process.wait()
print("✅ 连接已关闭")
defmain():
"""客户端测试主函数"""
client = SimpleMCPClient()
try:
# 1. 发送初始化请求
print("\n=== 步骤1: 初始化连接 ===")
response = client.send_request("initialize", {
"protocolVersion":"2025-03-26",
"capabilities": {"roots": {},"sampling": {}},
"clientInfo": {"name":"TestClient","version":"1.0.0"}
})
if"result"inresponse:
print("✅ 初始化成功!")
print(f"服务器信息:{response['result']['serverInfo']}")
# 2. 发送ping测试
print("\n=== 步骤2: 连接测试 ===")
response = client.send_request("ping")
if"result"inresponse:
print("✅ Ping测试成功!")
print(f"服务器响应:{response['result']['message']}")
# 3. 测试错误处理
print("\n=== 步骤3: 错误处理测试 ===")
response = client.send_request("unknown_method")
if"error"inresponse:
print("✅ 错误处理正常!")
print(f"错误信息:{response['error']['message']}")
exceptExceptionase:
print(f"❌ 测试失败:{e}")
finally:
client.close()
if__name__ =="__main__":
main()
▶️ 4. 运行测试
# 运行客户端测试
python mcp_client.py
你应该能看到类似这样的输出:
? 启动MCP客户端...
✅ 服务器进程已启动
=== 步骤1: 初始化连接 ===
? 发送请求: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 1,'method':'initialize','params': {...}}
? 收到响应: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 1,'result': {...}}
✅ 初始化成功!
服务器信息: {'name':'SimpleMCPServer','version':'1.0.0'}
=== 步骤2: 连接测试 ===
? 发送请求: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 2,'method':'ping'}
? 收到响应: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 2,'result': {'message':'pong','timestamp': 1703123456.789}}
✅ Ping测试成功!
服务器响应: pong
=== 步骤3: 错误处理测试 ===
? 发送请求: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 3,'method':'unknown_method'}
? 收到响应: {'jsonrpc':'2.0','id': 3,'error': {'code': -32601,'message':'Method not found: unknown_method'}}
✅ 错误处理正常!
错误信息: Method not found: unknown_method
? 关闭连接...
✅ 连接已关闭
5. 恭喜你
如果看到上面的输出,说明你已经成功搭建了一个完整的MCP系统!你刚刚完成了:
✅MCP服务器- 能够处理初始化、ping请求和错误处理
✅MCP客户端- 能够与服务器进行标准的JSON-RPC 2.0通信
✅Stdio传输- 通过标准输入输出进行进程间通信
✅错误处理- 标准的JSON-RPC错误代码和消息格式
总结与展望
通过本文的学习,我们深入了解了MCP协议的核心机制:
核心知识点回顾
- 架构理解- 客户端-服务器模式、协议层和传输层的分离设计
- 传输机制- Stdio传输的本质:进程间的标准输入输出重定向
- 协议规范- JSON-RPC 2.0的消息格式、错误处理和生命周期管理
技术价值
MCP协议的价值在于:
MCP协议作为AI应用的基础设施,正在快速发展。掌握这些核心概念,将为你在AI应用开发领域提供强大的技术基础。