|
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 1.2em;font-weight: bold;display: table;margin: 4em auto 2em;padding-right: 0.2em;padding-left: 0.2em;background: rgb(250, 81, 81);color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">LSTM 长短期记忆(Long Short-Term Memory)是一种时间循环神经网络(RNN),论文首次由施密德胡伯于1997年发表。 
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">由于独特的设计结构(三个门),LSTM适合于处理和预测时间序列中间隔和延迟非常长的重要事件。ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">LSTM的表现通常比时间循环神经网络及隐马尔科夫模型(HMM)更好,它们在时间序列预测、自然语言处理和语音识别等任务中特别有效。ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">LSTM 在很大程度上缓解了一个在 RNN 训练中非常突出的问题:梯度消失/爆炸(Gradient Vanishing/Exploding)。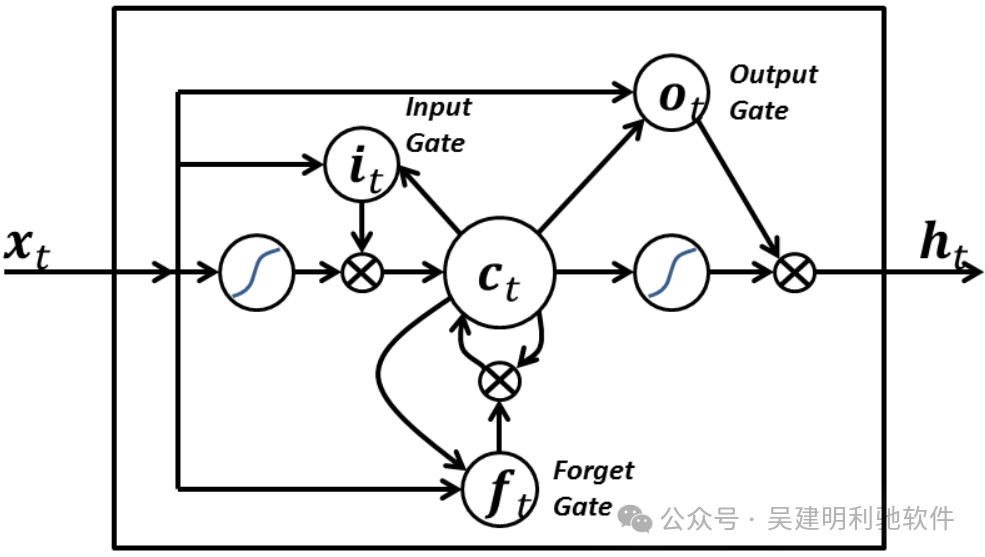
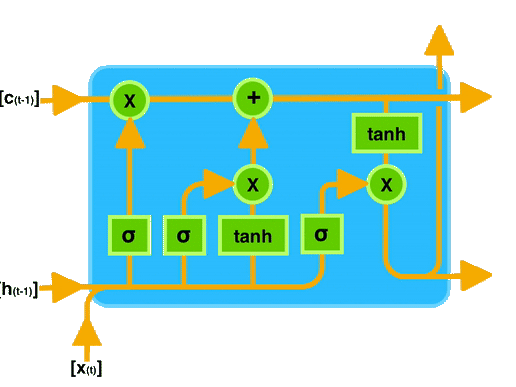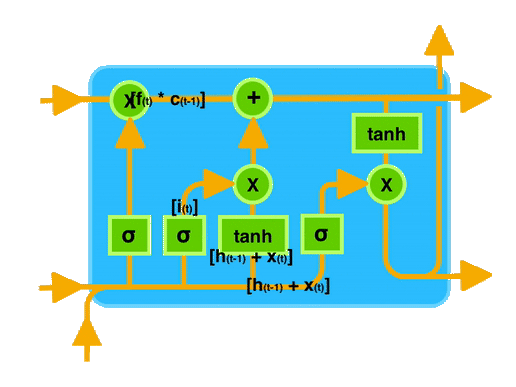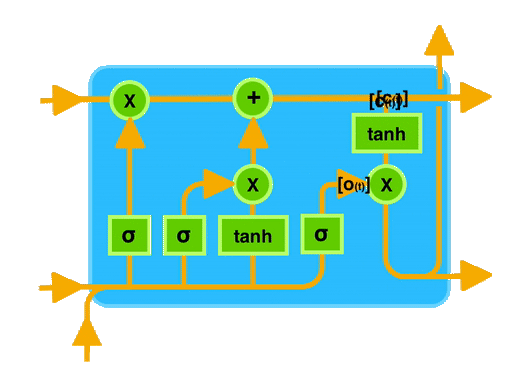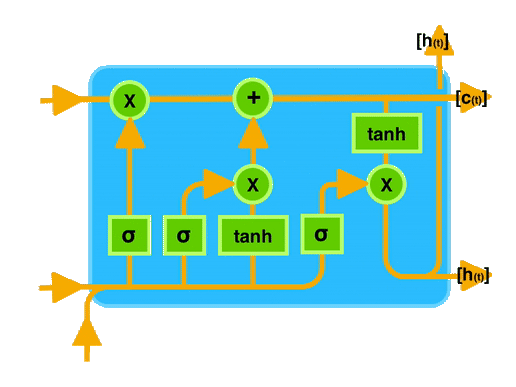
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">想象你在阅读一本小说,小说中有很多人物和情节,有些情节可能会影响后面的故事发展。LSTM 就像是一个能够记住之前发生的重要情节的人。当它阅读新的情节时,它会决定哪些情节是重要的需要记住,哪些可以忽略。这样,它就可以更好地理解整个故事,而不会因为记忆不足而丢失重要线索。ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">在计算机中,LSTM 类似于这个“记忆者”,可以帮助计算机更好地理解和处理序列数据,比如文本、语音等,尤其是那些需要长期记忆信息的任务。通过控制信息的流动,LSTM 能够更有效地学习和记忆长期依赖关系,从而提高模型在处理序列数据时的效果。ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 1.2em;font-weight: bold;display: table;margin: 4em auto 2em;padding-right: 0.2em;padding-left: 0.2em;background: rgb(250, 81, 81);color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">训练一个LSTM模型的完整步骤ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">一般来说,搭建文本生成模型的步骤包括:ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">1、准备文本数据,并进行预处理(如分词、标记化等)。ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;font-size: 16px;margin: 1.5em 8px;letter-spacing: 0.1em;color: rgb(63, 63, 63);">2、使用Tokenizer对文本进行编码。3、将文本数据转换为模型所需的输入格式(如序列数据)。 4、构建神经网络模型,包括Embedding层、LSTM层、Dense层等。 5、编译模型,指定损失函数、优化器和评估指标。 6、训练模型,可以使用fit方法,并设置一些参数(如批量大小、迭代次数等)。 7、使用训练好的模型生成文本。 本次数据是纽约时报数据集,包含了abstract摘要、headline标题、keywords关键词等等信息。 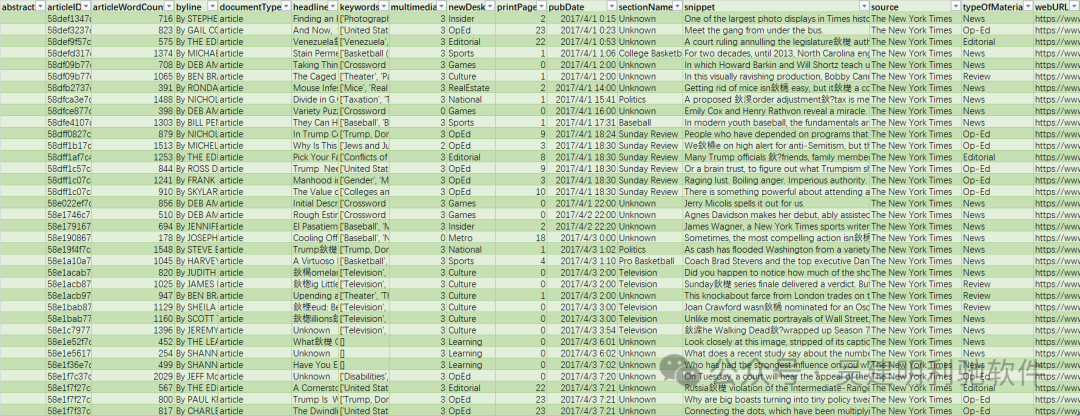
importnumpyasnp
importpandasaspd
importstring
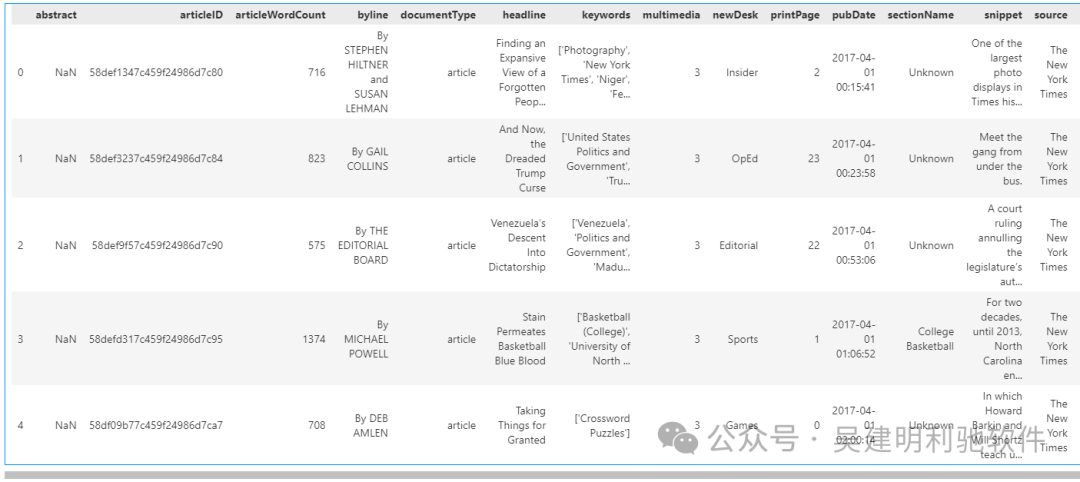
article_df=pd.read_csv(r".\ArticlesApril2017.csv")
article_df.head()
#将DataFrame中的文章标题(headline)提取出来,并添加到名为all_headlines的列表中。
all_headlines=[]
all_headlines.extend(list(article_df.headline.values))
all_headlines[:3]
输出:
['FindinganExpansiveViewofaForgottenPeopleinNiger',
'AndNow,theDreadedTrumpCurse',
'Venezuela’sDescentIntoDictatorship']
len(all_headlines)
886
#用于过滤掉all_headlines列表中值为"Unknown"的元素
all_headlines=[lineforlineinall_headlinesifline!="Unknown"]
len(all_headlines)
831
清洗数据 #清洁文本数据,去除文本中的标点符号,将文本转换为小写字母,并将文本编码为UTF-8再解码为ASCII编码
defclean_text(txt):
txt="".join(tfortintxtiftnotinstring.punctuation).lower()
txt=txt.encode('utf8').decode('ascii','ignore')
returntxt
corpus=[clean_text(x)forxinall_headlines]
print(corpus[:5])
输出:
['findinganexpansiveviewofaforgottenpeopleinniger',
'andnowthedreadedtrumpcurse',
'venezuelasdescentintodictatorship',
'stainpermeatesbasketballblueblood','takingthingsforgranted']
Tokenizer 类将文本转换为标记化的序列。 fromkeras.preprocessing.textimportTokenizer
fromkeras.modelsimportSequential
fromkeras.layersimportEmbedding,LSTM,Dense,Dropout
fromkeras.preprocessing.sequenceimportpad_sequences
importkeras.utilsasku
fromkeras.callbacksimportEarlyStopping
importtensorflowastf
tf.random.set_seed(2)
fromnumpy.randomimportseed
seed(1)
# Tokenizer 类可以帮助我们将文本转换为模型可以理解的数字表示形式,即将文本转换为标记化的序列。
tokenizer=Tokenizer()
定义了函数 get_sequence_of_tokens(corpus),将文本语料库转换为模型训练所需的输入序列。 defget_sequence_of_tokens(corpus):
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(corpus)
total_words=len(tokenizer.word_index)+1
input_sequences=[]
forlineincorpus:
token_list=tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([line])[0]
foriinrange(1,len(token_list)):
n_gram_sequence=token_list[:i+1]
input_sequences.append(n_gram_sequence)
returninput_sequences,total_words
#调用这行代码后,inp_sequences将包含生成的输入序列列表,total_words则是词汇表中的总单词数
inp_sequences,total_words=get_sequence_of_tokens(corpus)
print(inp_sequences[:10])
输出:
[[169,17],[169,17,665],[169,17,665,367],
[169,17,665,367,4],[169,17,665,367,4,2],
[169,17,665,367,4,2,666],[169,17,665,367,4,2,666,170],
[169,17,665,367,4,2,666,170,5],
[169,17,665,367,4,2,666,170,5,667],[6,80]]
#词汇表中的总单词数
print(total_words)
2422
函数 generate_padded_sequence 的作用是对输入序列列表进行填充处理,以便用于模型的训练。 defgenerate_padded_sequence(input_sequences):
max_sequence_len=max([len(x)forxininput_sequences])
input_sequences=np.array(pad_sequences(input_sequences,maxlen=max_sequence_len,padding='pre'))
predictors,label=input_sequences[:,:-1],input_sequences[:,-1]
label=ku.to_categorical(label,num_classes=total_words)
returnpredictors,label,max_sequence_len
predictors,label,max_sequence_len=generate_padded_sequence(inp_sequences)
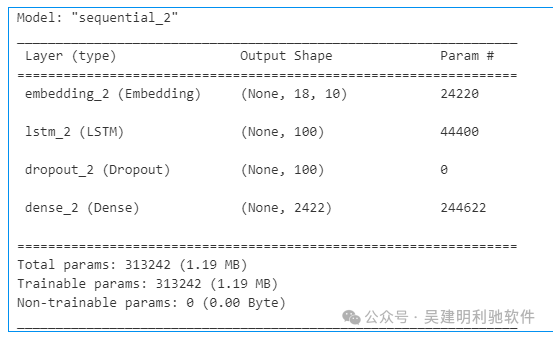
创建了一个神经网络模型 model。 defcreate_model(max_sequence_len,total_words):
input_len=max_sequence_len-1
model=Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(total_words,10,input_length=input_len))
model.add(LSTM(100))
model.add(Dropout(0.1))
model.add(Dense(total_words,activation='softmax'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy')
returnmodel
#创建了一个神经网络模型 model。这个模型将用于文本生成任务,其中 max_sequence_len 表示序列的最大长度,total_words 表示词汇表的大小。
model=create_model(max_sequence_len,total_words)
model.summary()
#使用 predictors 作为输入数据,label 作为标签数据,进行了10个 epochs 的训练,并设置 verbose=1 以显示训练过程中的详细信息。
model.fit(predictors,label,epochs=100,verbose=1)
定义函数 generate_text,用于生成文本序列。 defgenerate_text(seed_text,next_words,model,max_sequence_len):
for_inrange(next_words):
token_list=tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([seed_text])[0]
token_list=pad_sequences([token_list],maxlen=max_sequence_len-1,padding='pre')
predicted=model.predict(token_list,verbose=0)
classes_x=np.argmax(predicted,axis=1)
output_words=""
forword,indexintokenizer.word_index.items():
ifindex==classes_x:
output_word=word
break
seed_text=seed_text+""+output_word
returnseed_text.title()
最后验证: 1、generate_text("china",3,model,max_sequence_len)
输出:
'ChinaTakesAnInspiring.'
generate_text("china",10,model,max_sequence_len)
输出:
'ChinaTakesAInspiringTurnsToItsRiseOnCoalitionAirstrike.'
generate_text("china",30,model,max_sequence_len)
输出:
'ChinaTakesAInspiringTurnsToItsRiseOnCoalitionAirstrikePeopleYouSafetyDayTooReadersWithoutTrillionsNorthernTrillionsNorthernPickTrillionsAtPickThisTrillionsForDebateTrillions.'
这段文字一个混合了一些词语和短语的随机组合,有点胡说八道,产生“幻觉”问题。
2、generate_text("donaldtrump",30,model,max_sequence_len)
输出:
'DonaldTrumpPlaysAndTheNewYorkBeObamacareWorldEventBattleApartToPopulismFromFromMedicineTeachersThemAWhatsYorksDoorTodayTheBahamasFallsTimesTodayTodayWall'
3、generate_text("scienceandtechnology",5,model,max_sequence_len)
输出:
'ScienceAndTechnologyTheAmericansOfTheAmericans'
小结LSTM需要使用更大规模的数据集、引入外部知识库、设计更复杂的模型结构、引入对抗训练等,以改善大语言模型的生成质量和减少“幻觉”问题的出现。 |