|
ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;letter-spacing: normal;orphans: 2;text-align: start;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">关键技术、现有开源方案,提出并实现新方案ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">实现RAG面临挑战,尤其是在有效解析和理解非结构化文档中的表格方面。对于扫描文档或图像格式的文档,这一挑战尤为困难。这些挑战至少包括以下三个方面:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;letter-spacing: normal;orphans: 2;text-align: start;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;" class="list-paddingleft-1"> 扫描文档或图像文档的复杂性,如其多样化的结构、包含非文本元素以及手写与印刷内容的混合,给自动准确提取表格信息带来了挑战。解析不准确会破坏表格结构,使用不完整的表格进行嵌入不仅无法捕捉表格的语义信息,还容易破坏RAG的结果。 如何提取表格标题并有效关联到各自的表格。 如何设计索引结构以有效存储表格的语义信息。 ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">本文首先介绍RAG中管理表格的关键技术,然后回顾一些现有的开源解决方案,最后提出并实现一个新方案。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;letter-spacing: normal;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">关键技术ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;letter-spacing: normal;orphans: 2;text-align: start;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">表格解析ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">该模块的主要功能是从非结构化文档或图像中准确提取表格结构。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">附加功能:最好能提取相应的表格标题,并方便开发者将表格标题与表格关联。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">根据我目前的理解,有几种方法,如图1所示:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, serif;font-size: medium;font-style: normal;font-variant-ligatures: normal;font-variant-caps: normal;font-weight: 400;orphans: 2;text-indent: 0px;text-transform: none;widows: 2;word-spacing: 0px;-webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px;white-space: normal;text-decoration-thickness: initial;text-decoration-style: initial;text-decoration-color: initial;">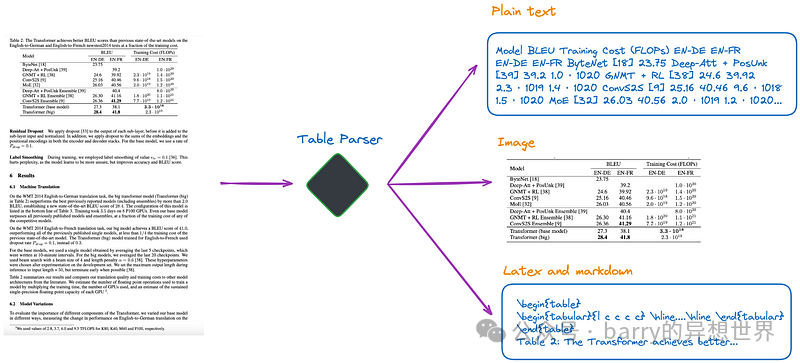 (a).利用多模态LLM,如GPT-4V,来识别表格并从每个PDF页面中提取信息。 (b).利用专业表格检测模型,如Table Transformer,来识别表格结构。 (c).使用开源框架,如unstructured等,这些框架也采用对象检测模型(unstructured的表格检测过程详见本文)。这些框架允许对整个文档进行全面解析,并从解析结果中提取与表格相关的内容。 (d).使用端到端模型,如Nougat、Donut等,来解析整个文档并提取与表格相关的内容。这种方法不需要OCR模型。 值得一提的是,无论使用哪种方法提取表格信息,都应包含表格标题。因为在大多数情况下,表格标题是文档或论文作者对表格的简要描述,可以大致概括整个表格。 在上述四种方法中,方法(d)可以方便地检索表格标题。这对开发者有益,因为它允许他们将表格标题与表格关联。这一点将在后续实验中进一步解释。 索引结构根据索引的结构,解决方案大致可以分为以下几类: (e).仅索引图像格式的表格。 (f).仅索引纯文本或JSON格式的表格。 (g).仅索引LaTeX格式的表格。 (h).仅索引表格的摘要。 (i).小到大或文档摘要索引结构,如图2所示。 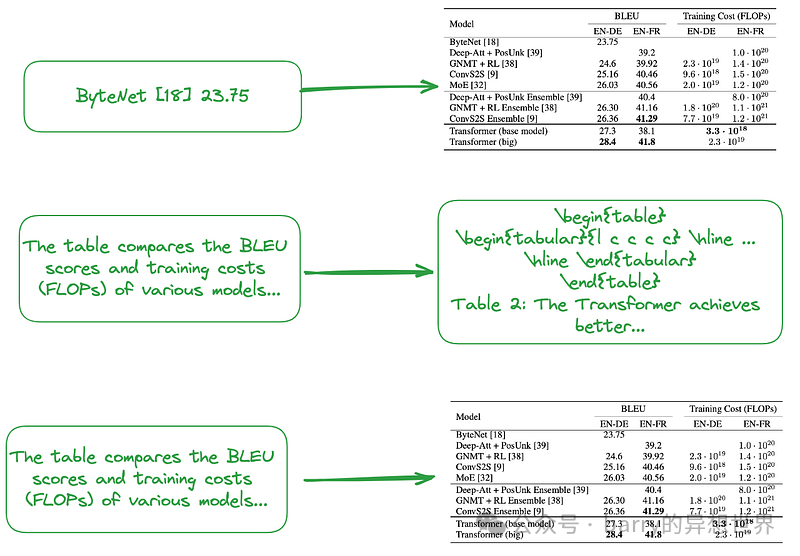
如上所述,表格摘要是通常使用LLM生成的: 输入:图像格式、文本格式或LaTeX格式的表格 输出:表格摘要
无需表格解析、索引或RAG的算法某些算法无需表格解析。 (j).将相关图像(PDF页面)和用户查询发送至VQA模型(如DAN等)或跨模态大型语言模型,并返回答案。 (k).将相关文本格式的PDF页面和用户查询发送至大型语言模型,然后返回答案。 (l).将相关图像(PDF页面)、文本片段和用户查询发送至跨模态大型语言模型(如GPT-4V等),并直接返回答案。 此外,以下是一些无需索引的方法,如图3和图4所示: 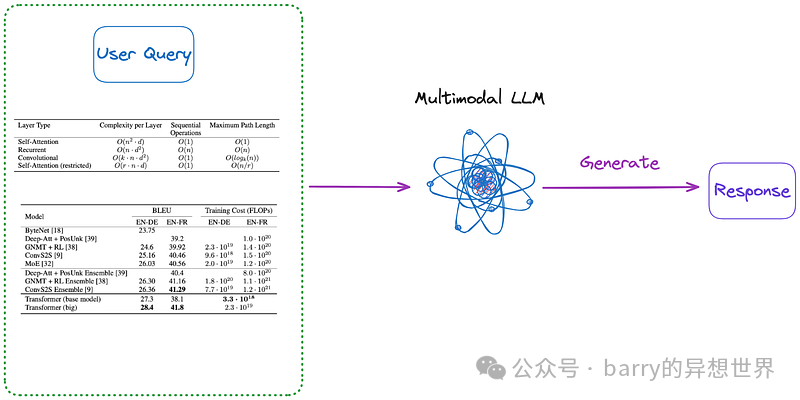
(m).首先,采用(a)至(d)类别中的任一方法,将文档中的所有表格解析为图像格式。然后直接将所有表格图像和用户查询发送至跨模态大型语言模型(如GPT-4V等)并返回答案。 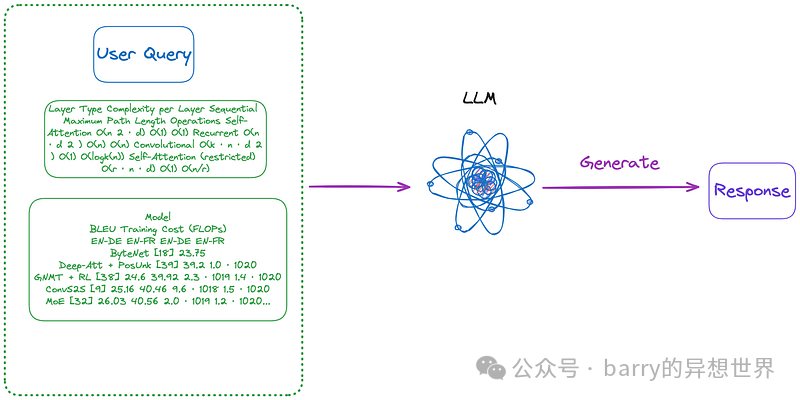
(n).使用(m)提取的图像格式表格,然后利用OCR模型识别表格中的所有文本,直接将表格中的所有文本和用户查询发送至大型语言模型并直接返回答案。 值得注意的是,某些方法不依赖于RAG流程: 现有开源解决方案上一节总结并分类了 RAG 中表格的关键技术。在提出本文实现的解决方案之前,我们先来探讨一些开源解决方案。 LlamaIndex 提出了四种方法,其中前三种使用了多模态模型。 检索相关图像(PDF 页面)并发送给 GPT-4V 以响应查询。 将每个 PDF 页面视为图像,让 GPT-4V 对每个页面进行图像推理。为图像推理构建文本向量存储索引。针对图像推理向量存储查询答案。 使用 Table Transformer 从检索到的图像中裁剪表格信息,然后将这些裁剪后的图像发送给 GPT-4V 以响应查询。 对裁剪后的表格图像应用 OCR,并将数据发送给 GPT4/GPT-3.5 以回答查询。
根据本文的分类: 第一种方法类似于本文的类别 (j),不需要表格解析。然而,结果显示,即使答案在图像中,也无法产生正确的答案。 第二种方法涉及表格解析,对应于类别 (a)。索引内容要么是表格内容,要么是根据 GPT-4V 返回的结果进行总结,这可能对应于类别 (f) 或 (h)。这种方法的缺点是 GPT-4V 识别表格并从图像中提取其内容的能力不稳定,特别是当图像包含表格、文本和其他图像的混合时,这在 PDF 格式中很常见。 第三种方法类似于类别 (m),不需要索引。 第四种方法类似于类别 (n),也不需要索引。其结果表明,由于无法从图像中提取表格信息,导致产生了错误的答案。
通过测试发现,第三种方法总体效果最好。然而,根据我的测试,第三种方法在检测表格方面存在困难,更不用说正确合并表格标题了。 Langchain 也提出了一些解决方案,Semi-structured RAG的关键技术包括: 如图 5 所示: 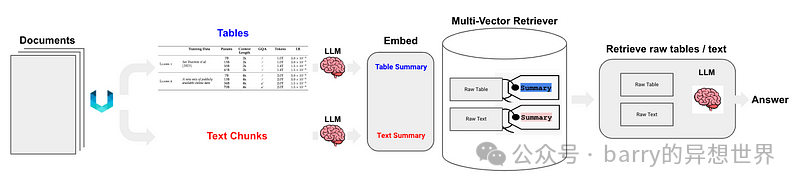
Semi-structured and Multi-modal RAG提出了三种解决方案,架构如图 6 所示。 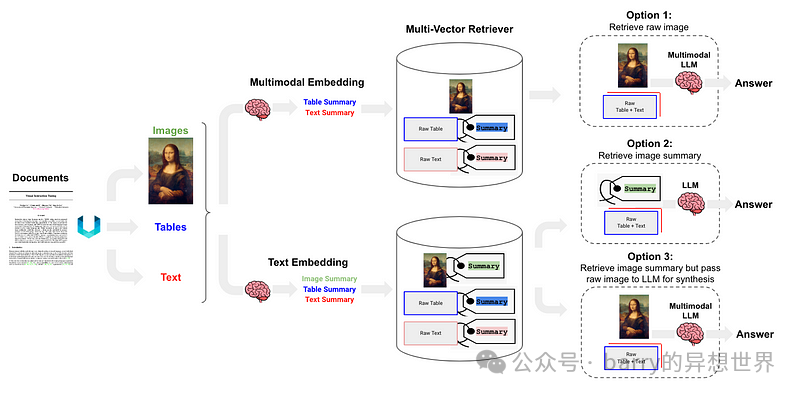
选项 1类似于本文的类别 (l)。它涉及使用多模态嵌入(如CLIP)来嵌入图像和文本,通过相似性搜索检索两者,并将原始图像和片段传递给多模态 LLM 进行答案合成。 选项 2利用多模态 LLM,如GPT-4V、LLaVA或FUYU-8b,从图像生成文本摘要。然后,嵌入并检索文本,并将文本片段传递给 LLM 进行答案合成。 选项 3使用多模态 LLM(如GPT-4V、LLaVA或FUYU-8b)从图像生成文本摘要,然后嵌入并检索图像摘要,并参考原始图像(类别 (i)),然后将原始图像和文本片段传递给多模态 LLM 进行答案合成。 提出的解决方案本文已对关键技术和现有解决方案进行了总结、分类和讨论。基于此,我们提出以下解决方案,如图7所示。为简化起见,省略了诸如重排序和查询重写等一些RAG模块。 
表格解析:使用Nougat(类别(d))。根据我的测试,其表格检测效果优于unstructured(类别(c))。此外,Nougat能很好地提取表格标题,非常便于与表格关联。 文档摘要索引结构(类别(i)):小数据块内容包括表格摘要,大数据块内容包括相应的LaTeX格式表格及文本格式表格标题。我们通过multi-vector retriever实现这一功能。 表格摘要获取方法:将表格及表格标题发送至LLM进行摘要生成。
此方法的优势在于,它高效解析表格的同时,全面考虑了表格摘要与表格之间的关系,并避免了多模态LLM的使用,从而节省了成本。 Nougat 原理Nougat基于Donut架构开发。它通过网络隐式识别文本,无需任何 OCR 相关输入或模块,如图 8 所示。 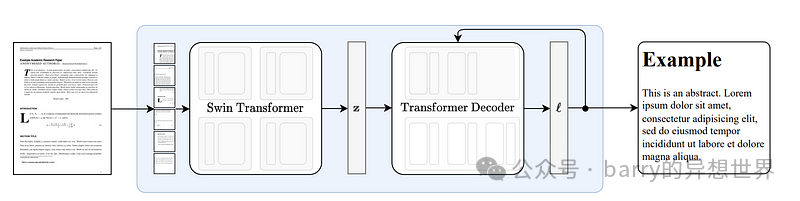
Nougat 解析公式的能力令人印象深刻。它在解析表格方面也同样出色。方便的是,它能够关联表格标题,如图 9 所示: 
在我测试的十几篇论文中,我发现表格标题总是固定在表格的下一行。这种一致性表明这不是偶然的。因此,我们感兴趣的是了解 Nougat 是如何实现这一效果的。 鉴于它是一个缺乏中间结果的端到端模型,它很可能严重依赖其训练数据。 根据训练数据格式化代码,对于表格,紧随**\end{table}**的行是**caption_parts**,这似乎与提供的训练数据格式一致: def format_element(
element: Element, keep_refs: bool = False, latex_env: bool = False
) -> List[str]:
"""
将给定元素格式化为格式化字符串列表。
参数:
element (Element): 要格式化的元素。
keep_refs (bool, 可选): 是否在格式化中保留引用。默认为 False。
latex_env (bool, 可选): 是否使用 LaTeX 环境格式化。默认为 False。
返回:
List[str]: 表示格式化元素的格式化字符串列表。
"""
...
...
if isinstance(element, Table):
parts = [
"[TABLE%s]\n\\begin{table}\n"
% (str(uuid4())[:5] if element.id is None else ":" + str(element.id))
]
parts.extend(format_children(element, keep_refs, latex_env))
caption_parts = format_element(element.caption, keep_refs, latex_env)
remove_trailing_whitespace(caption_parts)
parts.append("\\end{table}\n")
if len(caption_parts) > 0:
parts.extend(caption_parts + ["\n"])
parts.append("[ENDTABLE]\n\n")
return parts
...
...
诺格特的优缺点优点: 缺点: 诺格特的解析速度较慢,对于大规模部署可能构成挑战。 由于诺格特是在科学论文上训练的,因此在与类似结构的文档上表现出色。对于非拉丁文文本文档,其性能有所下降。 诺格特模型每次仅训练科学论文的一页,缺乏对其他页面的了解。这可能导致解析内容存在一些不一致性。因此,如果识别效果不佳,建议将PDF拆分为单独的页面并逐页解析。 在双栏论文中解析表格的效果不如单栏论文。
代码实现首先,安装相关的 Python 包 pip install langchain
pip install chromadb
pip install nougat-ocr
安装完成后,我们可以检查 Python 包的版本: langchain0.1.12
langchain-community0.0.28
langchain-core 0.1.31
langchain-openai 0.0.8
langchain-text-splitters 0.0.1
chroma-hnswlib 0.7.3
chromadb 0.4.24
nougat-ocr 0.1.17
设置环境并导入: import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPEN_AI_KEY"
import subprocess
import uuid
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.retrievers.multi_vector import MultiVectorRetriever
from langchain.storage import InMemoryStore
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
下载论文Attention Is All You Need到**YOUR_PDF_PATH**,运行 nougat 解析 PDF 文件,并从解析结果中获取 LaTeX 格式的表格和文本格式的表格标题。首次执行将下载必要的模型文件。 def june_run_nougat(file_path, output_dir):
# 运行 Nougat 并将结果存储为 Mathpix Markdown
cmd = ["nougat", file_path, "-o", output_dir, "-m", "0.1.0-base", "--no-skipping"]
res = subprocess.run(cmd)
if res.returncode != 0:
print("运行 nougat 时出错。")
return res.returncode
else:
print("操作完成!")
return 0
def june_get_tables_from_mmd(mmd_path):
f = open(mmd_path)
lines = f.readlines()
res = []
tmp = []
flag = ""
for line in lines:
if line == "\\begin{table}\n":
flag = "BEGINTABLE"
elif line == "\\end{table}\n":
flag = "ENDTABLE"
if flag == "BEGINTABLE":
tmp.append(line)
elif flag == "ENDTABLE":
tmp.append(line)
flag = "CAPTION"
elif flag == "CAPTION":
tmp.append(line)
flag = "MARKDOWN"
print('-' * 100)
print(''.join(tmp))
res.append(''.join(tmp))
tmp = []
return res
file_path = "YOUR_PDF_PATH"
output_dir = "YOUR_OUTPUT_DIR_PATH"
if june_run_nougat(file_path, output_dir) == 1:
import sys
sys.exit(1)
mmd_path = output_dir + '/' + os.path.splitext(file_path)[0].split('/')[-1] + ".mmd"
tables = june_get_tables_from_mmd(mmd_path)
函数**june_get_tables_from_mmd**用于从**mmd**文件中提取从**\begin{table}**到**\end{table}**的所有内容,包括**\end{table}**之后的行,如图 10 所示。 
值得注意的是,尚未找到官方文档指定表格标题必须位于表格下方或表格应以**\begin{table}**开始并以**\end{table}**结束。因此,**june_get_tables_from_mmd**是启发式的。 以下是解析 PDF 中表格的结果: 操作完成!
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
...
然后使用 LLM 总结表格: # 提示
prompt_text = """你是一个负责总结表格和文本的助手。\
给出表格或文本的简明总结。表格格式为 LaTeX,其标题为纯文本格式:{element}"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_text)
# 总结链
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature = 0, model = "gpt-3.5-turbo")
summarize_chain = {"element": lambda x: x} | prompt | model | StrOutputParser()
# 获取表格总结
table_summaries = summarize_chain.batch(tables, {"max_concurrency": 5})
print(table_summaries)
以下是Attention Is All You Need中找到的四个表格的总结,如图 11 所示: 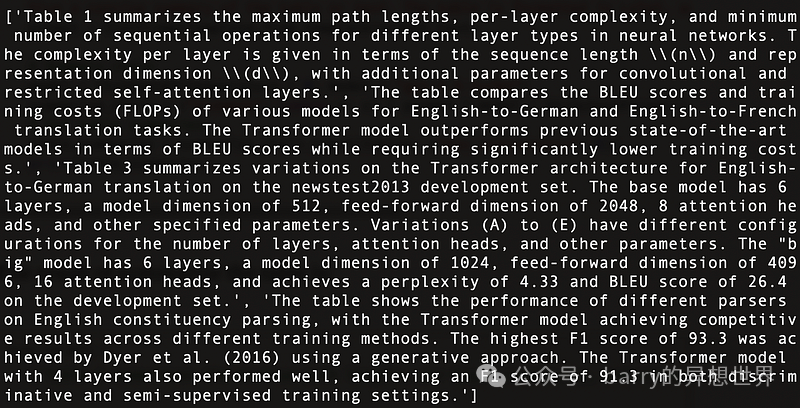
使用Multi-Vector Retriever构建文档总结索引结构。 # 用于索引子块的向量存储
vectorstore = Chroma(collection_name = "summaries", embedding_function = OpenAIEmbeddings())
# 父文档的存储层
store = InMemoryStore()
id_key = "doc_id"
# 检索器(初始为空)
retriever = MultiVectorRetriever(
vectorstore = vectorstore,
docstore = store,
id_key = id_key,
search_kwargs={"k": 1} # 解决请求的结果数 4 大于索引中元素数的问题,更新 n_results = 1
)
# 添加表格
table_ids = [str(uuid.uuid4()) for _ in tables]
summary_tables = [
Document(page_content = s, metadata = {id_key: table_ids[i]})
for i, s in enumerate(table_summaries)
]
retriever.vectorstore.add_documents(summary_tables)
retriever.docstore.mset(list(zip(table_ids, tables)))
一切准备就绪,构建一个简单的 RAG 管道并执行查询: # 提示模板
template = """仅根据以下上下文(可能包含文本和表格)回答问题,上下文中包含一个LaTeX格式的表格和一个纯文本格式的表格标题:
{context}
问题:{question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
# LLM
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature = 0, model = "gpt-3.5-turbo")
# 简单的RAG流程
chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)
print(chain.invoke("当层类型为Self-Attention时,每层的复杂度是多少?"))# 关于表1的查询
print(chain.invoke("哪个解析器在BLEU EN-DE上表现最差"))# 关于表2的查询
print(chain.invoke("哪个解析器在WSJ 23 F1上表现最好"))# 关于表4的查询
执行结果如下,展示了多个问题被准确回答,如图12所示: 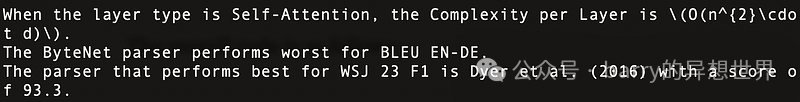
整体代码如下: import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPEN_AI_KEY"
import subprocess
import uuid
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.retrievers.multi_vector import MultiVectorRetriever
from langchain.storage import InMemoryStore
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
def june_run_nougat(file_path, output_dir):
# 运行Nougat并将结果存储为Mathpix Markdown
cmd = ["nougat", file_path, "-o", output_dir, "-m", "0.1.0-base", "--no-skipping"]
res = subprocess.run(cmd)
if res.returncode != 0:
print("运行nougat时出错。")
return res.returncode
else:
print("操作完成!")
return 0
def june_get_tables_from_mmd(mmd_path):
f = open(mmd_path)
lines = f.readlines()
res = []
tmp = []
flag = ""
for line in lines:
if line == "\\begin{table}\n":
flag = "BEGINTABLE"
elif line == "\\end{table}\n":
flag = "ENDTABLE"
if flag == "BEGINTABLE":
tmp.append(line)
elif flag == "ENDTABLE":
tmp.append(line)
flag = "CAPTION"
elif flag == "CAPTION":
tmp.append(line)
flag = "MARKDOWN"
print('-' * 100)
print(''.join(tmp))
res.append(''.join(tmp))
tmp = []
return res
file_path = "YOUR_PDF_PATH"
output_dir = "YOUR_OUTPUT_DIR_PATH"
if june_run_nougat(file_path, output_dir) == 1:
import sys
sys.exit(1)
mmd_path = output_dir + '/' + os.path.splitext(file_path)[0].split('/')[-1] + ".mmd"
tables = june_get_tables_from_mmd(mmd_path)
# 提示
prompt_text = """你是一个负责总结表格和文本的助手。\
请对表格或文本进行简要总结。表格采用LaTeX格式,其标题为纯文本格式:{element}"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_text)
# 总结流程
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature = 0, model = "gpt-3.5-turbo")
summarize_chain = {"element": lambda x: x} | prompt | model | StrOutputParser()
# 获取表格总结
table_summaries = summarize_chain.batch(tables, {"max_concurrency": 5})
print(table_summaries)
# 用于索引子块的向量存储
vectorstore = Chroma(collection_name = "summaries", embedding_function = OpenAIEmbeddings())
# 父文档的存储层
store = InMemoryStore()
id_key = "doc_id"
# 检索器(初始为空)
retriever = MultiVectorRetriever(
vectorstore = vectorstore,
docstore = store,
id_key = id_key,
search_kwargs={"k": 1} # 解决请求的结果数量4大于索引中的元素数量..., 更新n_results = 1
)
# 添加表格
table_ids = [str(uuid.uuid4()) for _ in tables]
summary_tables = [
Document(page_content = s, metadata = {id_key: table_ids[i]})
for i, s in enumerate(table_summaries)
]
retriever.vectorstore.add_documents(summary_tables)
retriever.docstore.mset(list(zip(table_ids, tables)))
# 提示模板
template = """仅根据以下上下文(可能包含文本和表格)回答问题,上下文中包含一个LaTeX格式的表格和一个纯文本格式的表格标题:
{context}
问题:{question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
# LLM
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature = 0, model = "gpt-3.5-turbo")
# 简单的RAG流程
chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)
print(chain.invoke("当层类型为Self-Attention时,每层的复杂度是多少?"))# 关于表1的查询
print(chain.invoke("哪个解析器在BLEU EN-DE上表现最差"))# 关于表2的查询
print(chain.invoke("哪个解析器在WSJ 23 F1上表现最好"))# 关于表4的查询
结论本文讨论了RAG流程中表格处理的关键技术和现有解决方案,并提出了一种解决方案及其具体实现。 我们在本文中使用nougat来解析表格。然而,如果有更快更有效的解析工具出现,我们也会考虑替换nougat。我们对工具的态度是先有正确的想法,再寻找工具来实现它,而不是依赖于某个特定工具。 在本文中,我们将所有表格内容输入到LLM中。但在实际场景中,我们应考虑到表格超出LLM上下文长度的情况。我们可以通过采用有效的分块方法来解决这一问题。
|