过去三年中, OpenAI 的 ChatGPT为代表的基础模型的出现显著加速了 LLM 应用的发展,但是如果只使用 LLM 依赖其“自有”知识来回答问题,往往会出现大模型幻觉,或者知识更新不及时等问题。基于这一背景,使用多个 LLM,每个 LLM 针对不同类型的问题进行优化的解决思路应运而生。但这也会出现一定的局限,那就是让整体系统变得复杂且难以扩展
过去三年中, OpenAI 的 ChatGPT为代表的基础模型的出现显著加速了 LLM 应用的发展,但是如果只使用 LLM 依赖其“自有”知识来回答问题,往往会出现大模型幻觉,或者知识更新不及时等问题。基于这一背景,使用多个 LLM,每个 LLM 针对不同类型的问题进行优化的解决思路应运而生。
但过多的模型拼合,又会导致整体系统变得复杂且难以扩展。那么,要如何解决这个问题呢?
答案是复合人工智能系统(CAIS)。接下来,我们将重点解读CAIS的历史演变以及搭建流程。
01.
CAIS的历史演变,从RAG到Agent
这一概念最早是2024年初加州大学伯克利分校的AI研究实验室网站上的一篇题为《从模型到复合人工智能系统的转变》的博客中被提及,它强调通过集成多种AI技术和模块来实现更高效、更可靠、更可解释的智能系统。
比如,我们可以通过在 LLM pipeline 中添加额外组件,进而提升系统性能。一个常见的代表是 RAG,RAG 通过将“知识库”或“上下文”存储在向量数据库(如 Milvus 或 Zilliz Cloud)中,并将其作为上下文与LLM结合,可以生成更准确、相关性更高的回答。
通常来说,构建 RAG 系统的基本步骤如下:
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Chunking:将文档拆分为较小的部分,以提高在向量数据库中用语义搜索内容的相关性,这是 Zilliz Cloud 和 Milvus 等向量数据库的核心特性。
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Embedding:将分块向量化(创建向量数值表示)并存入向量数据库。
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Prompt:向 LLM 提供指令,基于查询在向量数据库中检索以获取答案。
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">

图 1:RAG 的基本步骤
不难发现,以上各个环节,主要基于向量相似性进来完成检索以及内容生成,可一旦分块不够精准,或者分块后的内容与答案相关性不高,就会导致最终生成的答案也会不尽如人意。
与此同时,RAG的另一大局限性在于,对特定模型的过分依赖。比如,我们做一个比较任务,但模型可能是为归纳任务训练的。
在此基础上,Agent应运而生。
LLM Agent 是复杂的系统,它们通过在 pipeline 中添加了“类人”步骤,如推理、工具使用或规划,可以完成各种复杂操作。
比如,在下图中,LLM Agent 包含多个组件,它们可以在迭代过程中互动,不仅可以做相似性检索,还能完成包括规划、推理、工具使用和记忆等多种功能。
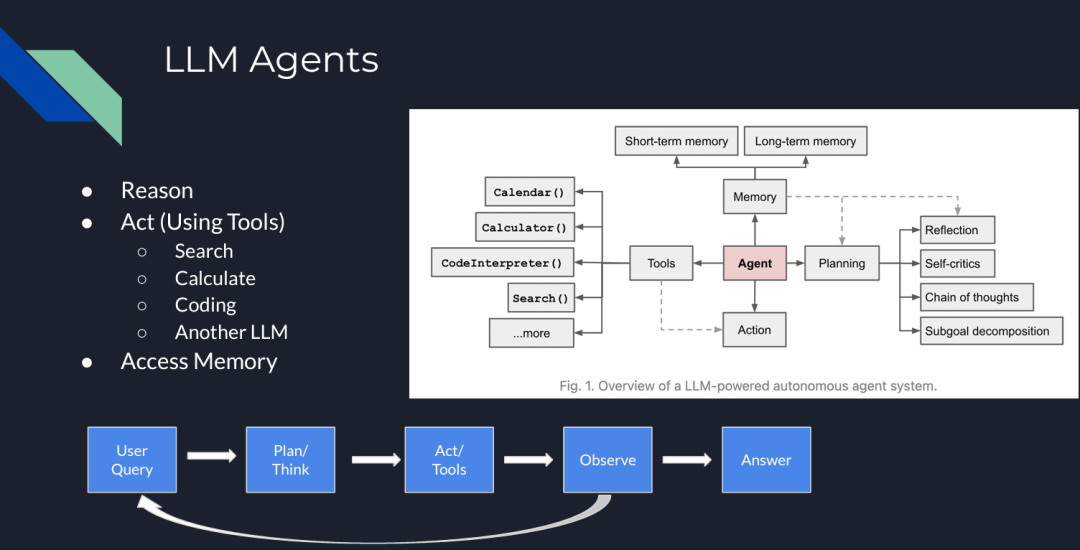
图 2:LLM Agents
目前各种 Agent 架构和框架中,最流行的是 ReAct(推理/行动)。其概念最早出自论文《ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models》。
在ReAct中,主要包括四个步骤:规划/推理(Plan/Think)、行动(act/tools)、评估(observe)和答案生成(answer)。
比较值得一提的是评估环节,在这一环节中,如果模型没有找到答案,它会返回推理步骤或要求用户给出更多额外提示来继续生成答案。

图 3:ReAct 框架
那么,我们如何在 RAG pipeline 中使用这些 Agent 呢?以下是在 RAG pipeline 中五种常见的智能体构建方式:
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Routing(路由):将用户查询重定向到与查询相关的特定知识库。
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Query Planning(查询规划):将查询拆分为子查询,每个子查询定向到相关的 RAG pipeline。
ingFang SC", "Hiragino Sans GB", "Microsoft YaHei UI", "Microsoft YaHei", Arial, sans-serif;letter-spacing: 1px;">Tool Use(工具使用):LLM 与外部 API 或工具交互,确定交互所需的参数。
ReAct:一个迭代过程,结合推理和行动,包括规划、工具使用和观察步骤。
示例:为了生成详细的旅行行程,系统推理用户需求,使用 API 收集景点、餐饮和住宿信息,观察结果的准确性和相关性,然后提供全面的旅行计划。
Dynamic Query Planning(动态查询规划):Agent 并行执行多个任务或子查询,而不是顺序执行,并聚合结果。
示例:如果您想比较两家公司的财务结果并计算特定指标的差异,Agent 会并行处理两家公司的数据,然后合并结果以提供比较。LLMCompiler 是一个示例框架,支持高效且有效地编排并行函数调用。

图 4:LLM 编译器
现在,让我们搭建一个使用 Milvus 向量数据库的简单 Agentic pipeline。
02.
使用 Claude 3.5 Sonnet、LlamaIndex 和 Milvus 构建 Agentic RAG
以下内容是一个使用 LlamaIndex 作为 Agent 框架、Milvus 作为向量数据库、Claude 3.5 Sonnet 作为 LLM 的 Agentic RAG peipeline示例,我们将用其构建一个 Agentic RAG。
步骤 1:数据加载
我们使用 Milvus documentation 2.4.x 的 FAQ 页面作为 RAG 的私有知识库。
!pipinstall-qqllama-indexpymilvusllama-index-vector-stores-milvusllama-index-llms-anthropic
!wgethttps://github.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/releases/download/v2.4.6-preview/milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip
!unzip-q/content/milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip-d/content/milvus_docs
fromllama_index.coreimportSimpleDirectoryReader
#loaddocuments
documents=SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_files=["/content/milvus_docs/en/faq/operational_faq.md"]
).load_data()
print("DocumentID:",documents[0].doc_id)
步骤 2:环境变量
我们需要导入两个 API 密钥:Anthropic 和 OpenAI。
importos
fromgoogle.colabimportuserdata
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"]=userdata.get('ANTHROPIC_API_KEY')
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]=userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
步骤 3:数据索引
使用 Milvus 向量数据库创建文档索引,作为我们的知识库。由于 OpenAI 是 LlamaIndex 中的默认 embedding 模型(可以更改),我们需要在 MilvusVectorStore 中定义相同的维度(dim = 1536)。运行以下代码后,将创建一个本地数据库,其中包含我们的知识库。
fromllama_index.coreimportVectorStoreIndex,StorageContext
fromllama_index.vector_stores.milvusimportMilvusVectorStore
vector_store=MilvusVectorStore(dim=1536)
storage_context=StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
index=VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents,storage_context=storage_context)
步骤 4:简单查询引擎
首先测试没有 Agent 的查询引擎。它由 Claude 3.5 Sonnet 提供支持,并在我们的索引中搜索相关内容。
llm=Anthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620")
query_engine=index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5,llm=llm)
res=query_engine.query("WhatisthemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvus?")
print(res)
"""
Output:
Milvussupportsvectorswithupto32,768dimensionsbydefault.However,ifyouneedtoworkwithvectorsofevenhigherdimensionality,youhavetheoptiontoincreasethevalueofthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameter.ThisallowsMilvustoaccommodatevectorswithdimensionsexceedingthedefaultlimit.
"""
步骤 5:Agent 查询引擎
现在,我们添加 QueryEngineTool,它将作为查询引擎的包装工具,供 Agent 使用。
fromllama_index.coreimportVectorStoreIndex
fromllama_index.core.toolsimportQueryEngineTool,ToolMetadata
fromllama_index.llms.anthropicimportAnthropic
llm=Anthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620")
query_engine=index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5,llm=llm)
query_engine_tool=QueryEngineTool(
query_engine=query_engine,
metadata=ToolMetadata(
name="knowledge_base",
description=("ProvidesinformationaboutMilvusFAQ.""Useadetailedplaintextquestionasinputtothetool."
),
),
)
步骤 6:AI Agent 创建
本例中使用的 Agent 是 LlamaIndex 的 FunctionCallingAgentWorker,它在查询回复上部署 critic reflection,利用查询引擎工具生成改进的答案。
fromllama_index.core.agentimportFunctionCallingAgentWorker
agent_worker=FunctionCallingAgentWorker.from_tools(
[query_engine_tool],llm=llm,verbose=True
)
agent=agent_worker.as_agent()
response=agent.chat("WhatisthemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvus?")
print(str(response))
"""
Output:
Addedusermessagetomemory:WhatisthemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvus?
===LLMResponse===
ToansweryourquestionaboutthemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvus,I'llneedtoconsulttheMilvusFAQknowledgebase.Letmedothatforyou.
===CallingFunction===
Callingfunction:knowledge_basewithargs:{"input":"WhatisthemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvus?"}
===FunctionOutput===
Milvussupportsvectorswithupto32,768dimensionsbydefault.However,ifyouneedtoworkwithvectorsofevenhigherdimensionality,youhavetheoptiontoincreasethevalueofthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameter.ThisallowsMilvustoaccommodatevectorswithdimensionsexceedingthedefaultlimit.
===LLMResponse===
BasedontheinformationfromtheMilvusFAQknowledgebase,Icanprovideyouwiththefollowinganswer:
ThemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvusis32,768bydefault.Thismeansthatoutofthebox,Milvuscanhandlevectorswithupto32,768dimensions,whichissuitableformostapplications.
However,it'simportanttonotethatMilvusoffersflexibilityforcaseswhereyoumightneedtoworkwithevenhigher-dimensionalvectors.Ifyourusecaserequiresvectorswithdimensionsexceeding32,768,youhavetheoptiontoincreasethislimit.Thiscanbedonebyadjustingthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameterinMilvusconfiguration.
So,tosummarize:
1.Defaultmaximumdimension:32,768
2.Canbeincreased:Yes,bymodifyingthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameter
ThisflexibilityallowsMilvustoaccommodateawiderangeofusecases,fromtypicalmachinelearningandAIapplicationstomorespecializedscenariosthatmightrequireextremelyhigh-dimensionalvectors.
BasedontheinformationfromtheMilvusFAQknowledgebase,Icanprovideyouwiththefollowinganswer:
ThemaximumvectordimensionsupportedinMilvusis32,768bydefault.Thismeansthatoutofthebox,Milvuscanhandlevectorswithupto32,768dimensions,whichissuitableformostapplications.
However,it'simportanttonotethatMilvusoffersflexibilityforcaseswhereyoumightneedtoworkwithevenhigher-dimensionalvectors.Ifyourusecaserequiresvectorswithdimensionsexceeding32,768,youhavetheoptiontoincreasethislimit.Thiscanbedonebyadjustingthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameterinMilvusconfiguration.
So,tosummarize:
1.Defaultmaximumdimension:32,768
2.Canbeincreased:Yes,bymodifyingthe'Proxy.maxDimension'parameter
ThisflexibilityallowsMilvustoaccommodateawiderangeofusecases,fromtypicalmachinelearningandAIapplicationstomorespecializedscenariosthatmightrequireextremelyhigh-dimensionalvectors.
"""
Agent 的输出提供了更详细的答案,包括信息来源、答案背后的推理过程以及一些与话题相关的额外建议。这帮助我们更好地理解 LLM 模型给出的答案。
03.
Agentic RAG 架构
我们刚刚构建的 Agentic RAG 的完整架构如下所示。

图 5:使用 Milvus、LlamaIndex 和 Claude 3.5 Sonnet 构建的 Agentic RAG 架构
04.
结论
Compund AI 的概念将复杂的人工智能系统分解为多个独立的模块,进而带来了更多的灵活性、可扩展性、可复用性,并降低了系统耦合度,极大提升了 pipeline 的整体效率。沿着这一理念, LLM 系统的演变,经历了从独立模型到结合 RAG 和 Agent 的更复杂架构的转变。
而在此过程中,Milvus为代表的向量数据库技术通过提供强大的数据管理、检索和融合能力,显著提升了系统的效率、准确性和可靠性。它不仅优化了 RAG 和 Agent 等模块的性能,还为多模态数据处理和实时决策提供了支持,并极大提升了系统的灵活性和可扩展性。