当前 AI 系统面临的核心挑战是数据接入的碎片化问题。企业和开发者在对接不同数据源时,往往需要为每个系统单独开发定制化的对接方案。这种重复性工作开发成本太高了,而且系统间难以实现真正的互联互通。
Claude 的 MCP 协议正就是为了解决这一行业痛点而生的,它是是由 Anthropic 开发的、针对人工智能 (AI) 模型的一种通信协议。MCP 代表“Message Communication Protocol”(消息通信协议)。该协议的设计旨在增强 AI 系统的消息传递能力,促进不同系统之间的协调与合作。
核心理念:
架构
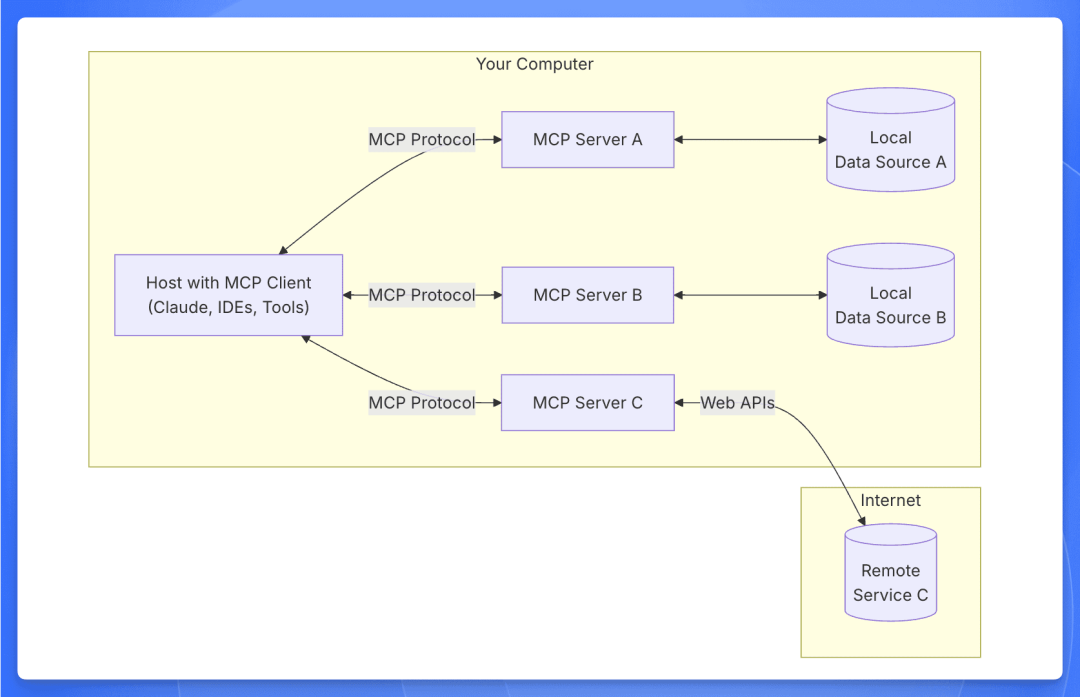
MCP 协议由一个 client 和多个 server 组成。用户发出请求后,client 会去调用 server 执行逻辑并返回给用户。
client 就是用户的对话框,server 是一些我们提前写好的代码,用来完成我们想实现的系统调用。client 和 server 都可以自行开发。
核心概念
工具 (Tools)
工具是服务器编写,可由客户端调用并由 LLM 用来执行操作的可执行函数。
当前对其支持较多,主要的逻辑都通过工具来实现。
提示 (Prompts)
可以理解为预设好的提示词模版,用于补充用户的输入。
假设用户输入的是:
def add(a, b):
return a + b
生成的提示可能是:
Explain how this Python code works:
def add(a, b):
return a + b
当前对其的支持相对较少。
资源 (Resources)
提供服务端的资源给客户端。
文件内容
数据库记录
API 响应
实时系统数据
截图和图片
日志文件
更多内容
当前对其支持相对较少,一般只有客户端显示调用的时候才会使用。
工作流程
MCP 的工作流程可以在这里找到:https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/python-sdk/tree/main/examples/clients/simple-chatbot
简单总结如下:
初始化:客户端访问服务端的接口,获取 tools,prompts,resources 等资源。
客户端接收用户输入,并携带着上述资源的上下文一起发送给大模型
客户端判断通过大模型输出判断是否需要调用资源,如果需要就去调用,并把调用的结果返回给大模型
大模型分析,整合结果后返回给客户端。
提示词
官方 demo 中的提示词如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
system_message = (
"You are a helpful assistant with access to these tools:\n\n"
f"{tools_description}\n"
"Choose the appropriate tool based on the user's question. "
"If no tool is needed, reply directly.\n\n"
"IMPORTANT: When you need to use a tool, you must ONLY respond with "
"the exact JSON object format below, nothing else:\n"
"{\n"
'"tool": "tool-name",\n'
'"arguments": {\n'
'"argument-name": "value"\n'
"}\n"
"}\n\n"
"After receiving a tool's response:\n"
"1. Transform the raw data into a natural, conversational response\n"
"2. Keep responses concise but informative\n"
"3. Focus on the most relevant information\n"
"4. Use appropriate context from the user's question\n"
"5. Avoid simply repeating the raw data\n\n"
" lease use only the tools that are explicitly defined above."
lease use only the tools that are explicitly defined above."
)
使用 MCP,我们需要:
下面使用 Claude 模型,使用 Claude Desktop 作为 MCP Client,自己开发 MCP Server 进行使用。(也可以直接使用官方的 MCP Server)
Server 开发流程
使用 python sdk 开发,前置需要 Mac,并安装 python uv 和 claude desktop。
官网给出的开发流程:https://modelcontextprotocol.io/quickstart/server
创建环境
使用 uv 创建开发环境
# Create a new directory for our project
uv init 项目名
cd 项目名
# Create virtual environment and activate it
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
uv add "mcp[cli]" httpx
编写 mcp server 代码
官网上有 demo (https://modelcontextprotocol.io/quickstart/server) 可以直接丢给大模型仿照这个写。
写提示词的时候要注意下 mcp server 的提示词来源,阅读源代码发现它有两种方式:用户手动指定 description,就是自己写提示词,如果用户不手动指定的话,就默认使用 mcp server 代码的注释作为提示词。
配置 claude desktop
编写完代码,测试能成功运行之后,需要修改 claude desktop 的配置使其识别到这个 server,配置路径:
~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
配置的格式
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/Users/wpy/downloads/mcp-test",
"run",
"hello.py"
]
}
}
}
保存并退出之后,重启 claude desktop,就能看到对话框的右下角出现一个锤子标志:
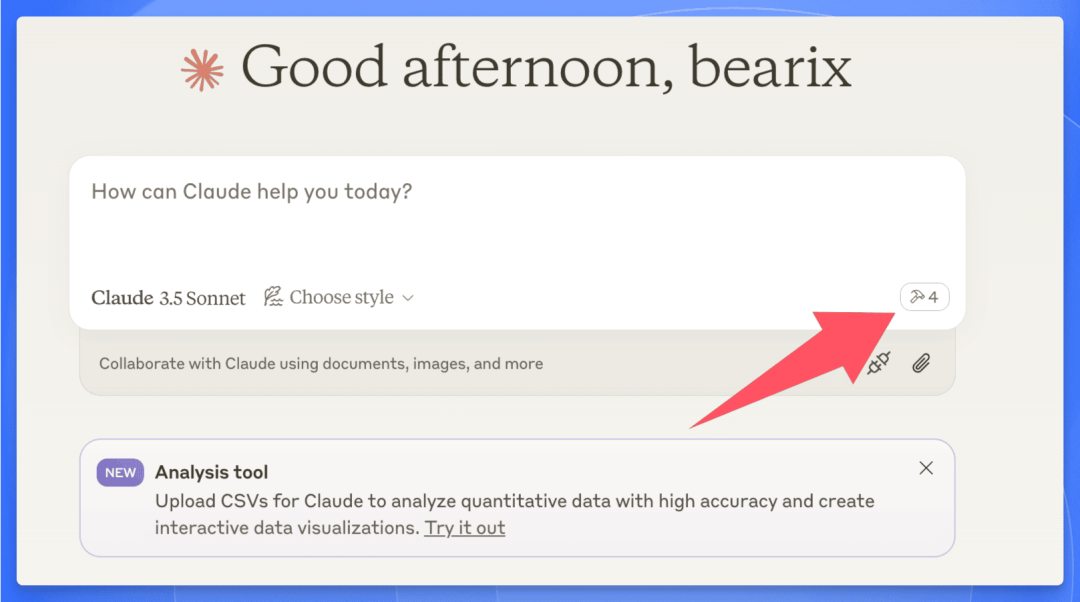
出现这个标志就表明 desktop 已经识别到了编写的 server,接下来就可以开始使用了。
针对提出的问题,模型会自主判断是否要使用这些 server,并在使用的时候发出提示:
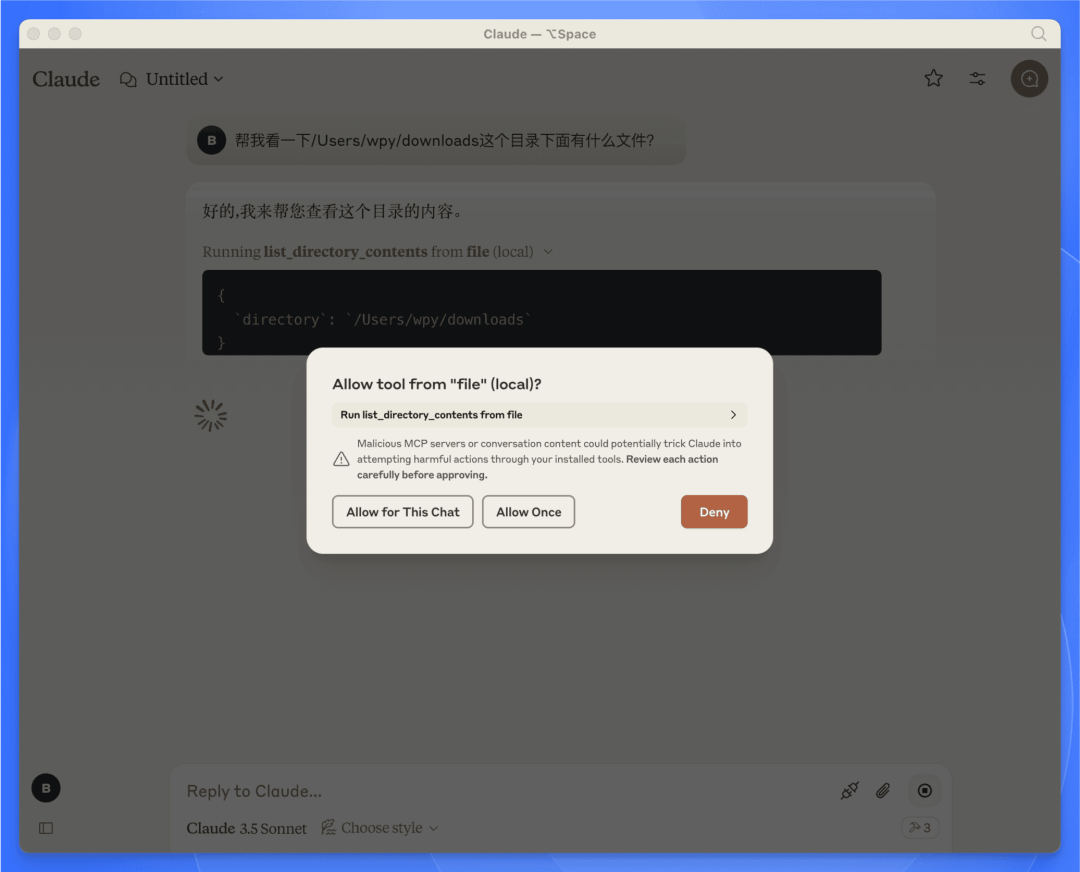
Server demo1:查看本地文件
实现
MCP Server 运行在本地,直接访问本地的文件。
server 代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
import os
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("file")
@mcp.tool()
async def list_directory_contents(directory: str) -> str:
"""List the contents of a directory.
Args:
directory: The path of the directory to list.
"""
try:
# Get the list of files and directories in the specified path
directory_contents = os.listdir(directory)
if not directory_contents:
return "The directory is empty."
# Format the contents into a readable list
contents = "\n".join(directory_contents)
return f"Contents of {directory}:\n{contents}"
except FileNotFoundError:
return f"Directory {directory} not found."
except PermissionError:
return f" ermission denied to access {directory}."
ermission denied to access {directory}."
except Exception as e:
return f"An error occurred: {str(e)}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
claude desktop 的配置文件:
{
"file": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/Users/wpy/downloads/file-mcp",
"run",
"hello.py"
]
}
}
}
效果
可以查看本地目录下的文件。
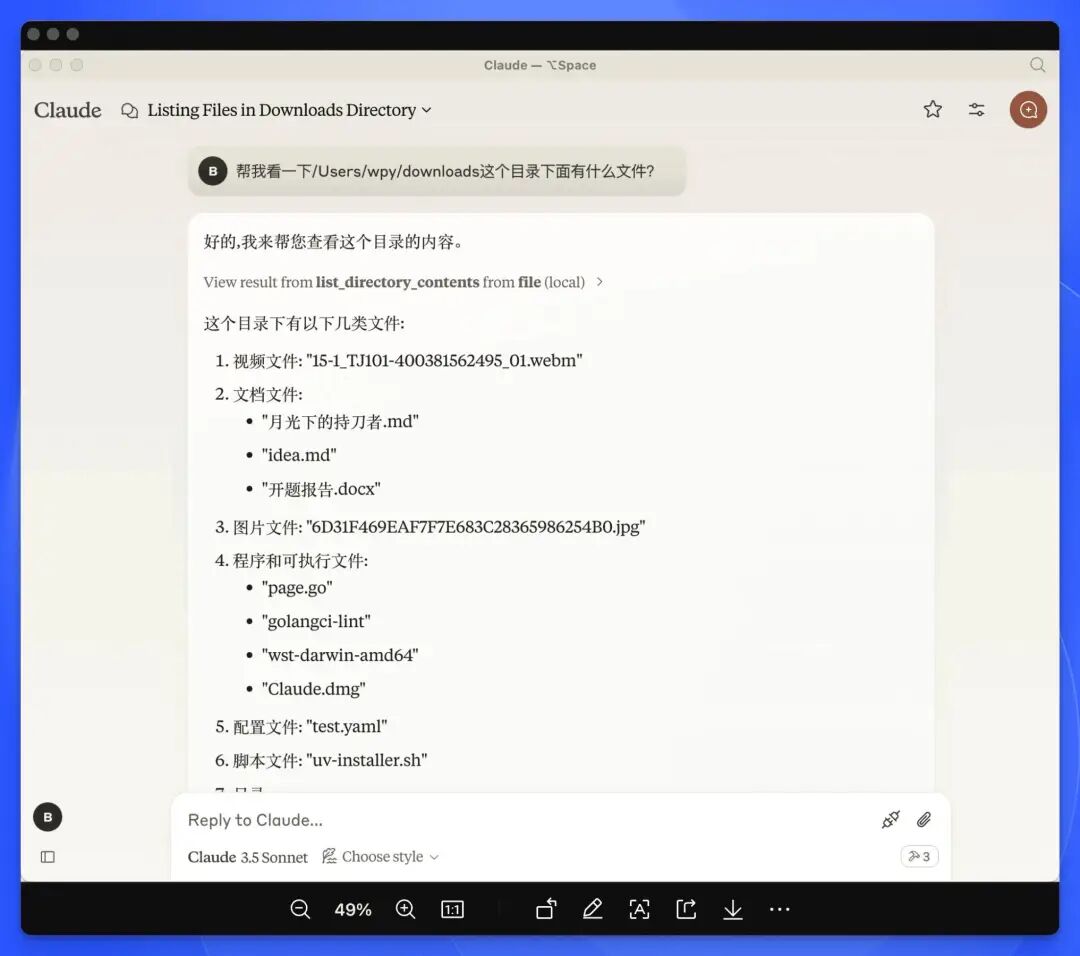
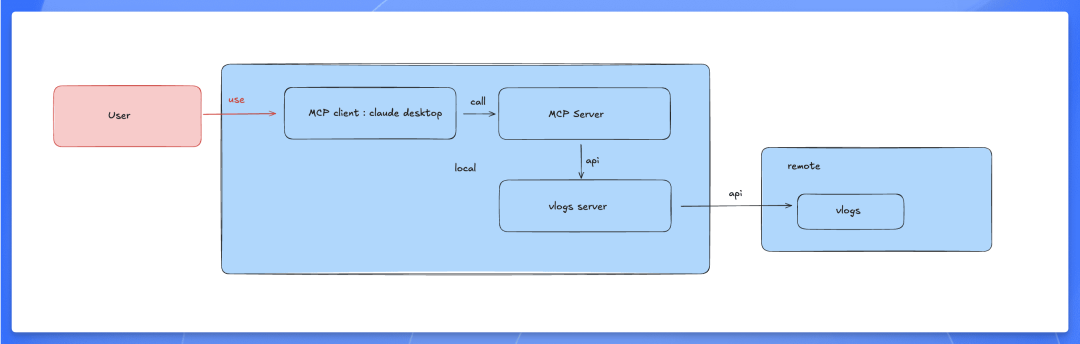
Server demo2:查询 vlogs 日志
实现
本地运行 vlogs server,通过 MCP 的 Server 去访问。
server 代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
import os
import requests
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("file")
# Define the URL for the API endpoint
API_URL = "http://localhost:8428/queryLogsByParams"
HEADERS = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer my-token"
}
@mcp.tool()
async def get_logs(time: str, namespace: str, app: str, limit: str, pod: list, container: list, keyword: str) -> str:
"""Get logs from the API by passing parameters.
Args:
time: The time filter for logs (e.g., "10h").
namespace: The namespace of the application (e.g., "gpu-operator").
app: The name of the application (e.g., "gpu-operator").
limit: The limit for the number of logs to retrieve.
pod: The list of pods to query.
container: The list of containers to query.
keyword: The keyword to filter logs by.
"""
data = {
"time": time,
"namespace": namespace,
"app": app,
"limit": limit,
"jsonMode": "false",
"stderrMode": "true",
"numberMode": "false",
"numberLevel": "h",
"pod": pod,
"container": container,
"keyword": keyword,
"jsonQuery": []
}
try:
# Make the POST request to the API
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=HEADERS, json=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
# If the request was successful, return the log data
return f"Logs retrieved successfully:\n{response.text}"
else:
return f"Failed to retrieve logs. Status code: {response.status_code}"
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return f"An error occurred while accessing the API: {str(e)}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
claude desktop 的配置文件:
{
"mcpServers": {
"vlogs-server": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/Users/wpy/downloads/vlogs-mcp",
"run",
"hello.py"
]
}
}
}
效果
可以实现使用 AI 查询并分析用户的日志。
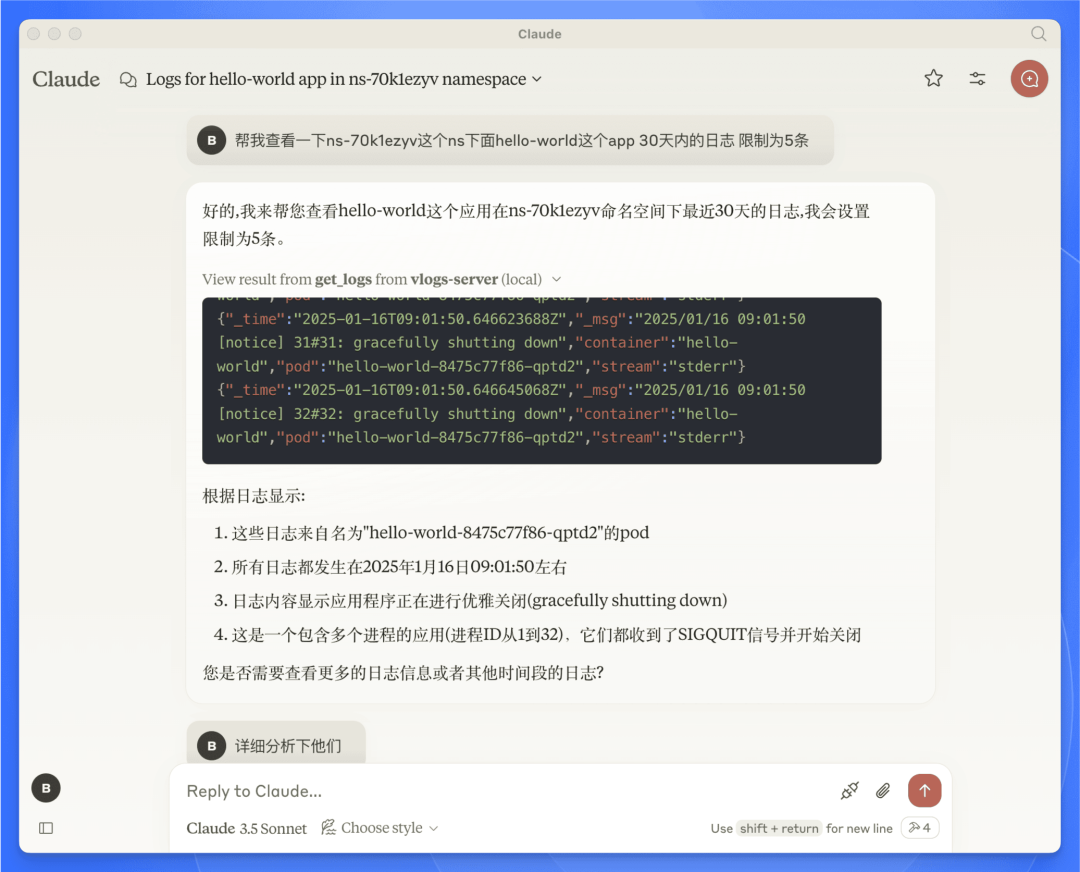
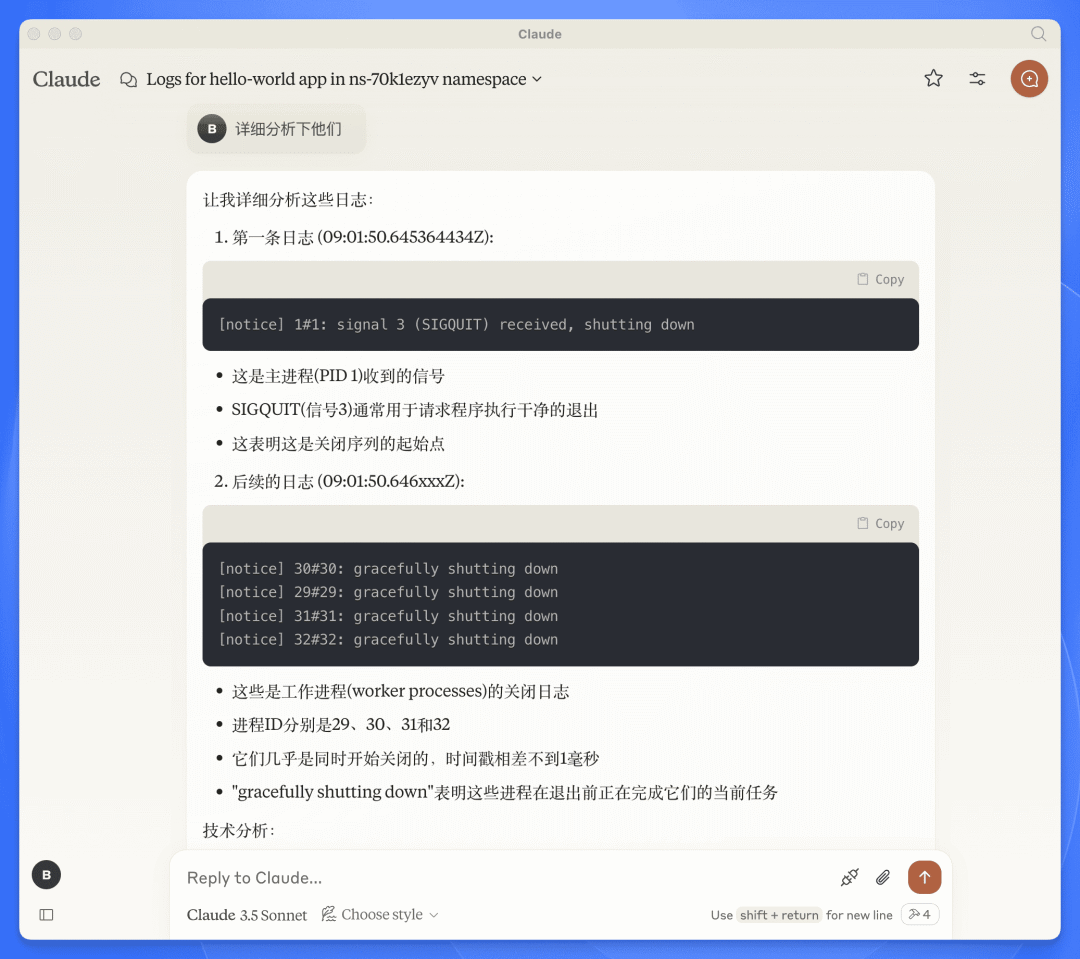
从效果上看,可以满足我们的部分需求。
总结
从效果上看,像上面的 demo 一样,开发一套 MCP Server 和 Client 可以满足我们的部分需求,实现 AI 的工程化接入。
能实现的需求包括:
AI 查询和分析日志
AI 管理应用,数据库,Devbox 的生命周期
还可以根据其官方和社区提供的各种 MCP Server 思考新的功能

官方 SDK 存在的问题
之前的 demo 中 MCP Server 的开发都依赖了官方的 SDK,但是官方的 SDK 存在一些问题
后续迭代思路
依赖官方 SDK,开发 MCP Server 和 Client
可以通过一些操作解决之前提到的问题,而不重写 SDK。
关于多模型:参考 cline,在 client 前面加一个兼容层 (本质也是在 client 里调用模型,server 只提供数据和进行工具调用),就可以支持多模型
关于远程环境问题:不需要使用远程环境,mcp client 和 mcp server 都放在本地
关于权限认证问题:存到本地的一个配置文件即可,比如 kc,token 之类的
关于计费问题:软件本身使用不计费,AI proxy 计费大模型 token,然后操作 Sealos 能力引流 Sealos
总结:本地 AI-Coding 就在 cline 基础上内置一些 MCP 和环境信息,Web 网站上就在 Nextjs 端做一下 MCP 即可。
根据官方的 SDK 重写,然后开发 MCP Server 和 Client
claude 的 SDK 都开源了 (例如 python-sdk 位于 https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/python-sdk),可以仿照开发出其他语言的 SDK。
通过重写 SDK,可以把 MCP Server 放在远程并支持其他模型,用户本地不需要安装一堆的 server,除了一个 client,其他都放在远程:
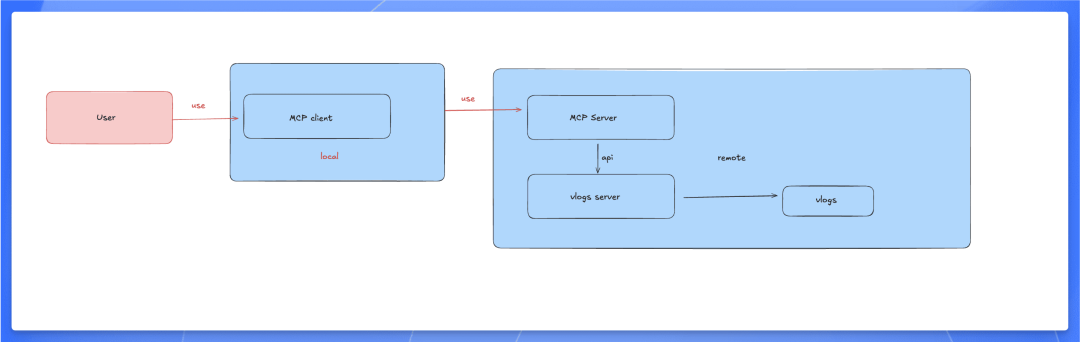
采用这个方案,成本更高,但是可以完全符合我们的需求,并且可以考虑后续和其官方社区合作。
不使用 mcp 协议,选用其他方案
MCP 协议稍微有点复杂,不过其中的一些设计理念可以参考。