|
大模型在面对实行性、私域知识型问题或数学计算等问题时可能效果不佳,如查询天气,连续搜索引擎查询等。最常使用的解决方式就是直接调用外部工具来提升模型的输出效果。
大纲:qwen请求的介绍
使用工具的流程一、通过官方例子实现二、通过langchain实现
有些模型是不支持调用工具的,下面我们看下qwen调用工具的参数要求,其实就是在参数中声明role为tool。 qwen请求的介绍
tool参数用于指定可供模型调用的工具库,一次function call流程模型会从中选择其中一个工具。tools中每一个tool的结构如下: 使用tools时需要同时指定result_format为message。在function call流程中,无论是发起function call的轮次,还是向模型提交工具函数的执行结果,均需设置tools参数。当前支持的模型包括qwen-turbo、qwen-plus、qwen-max和qwen-max-longcontext。 说明 tools暂时无法和incremental_output参数同时使用。
使用工具的流程大概使用的工具的流程是,首先我们向大模型提出问题,在提问之前我们要把使用的工具配置和用户提的问题一起发送给大模型,工具的配置一般都会有工具的名称和参数,还有对工具的描述,这几个参数是很重要的。大模型拿到数据后,会根据用户提的问题判断应该调用哪个工具,之后会把调用的工具的信息返回给我们的程序,程序再根据工具名称判断调用哪个工具,拿到结果之后再二次发送给模型进行加工。 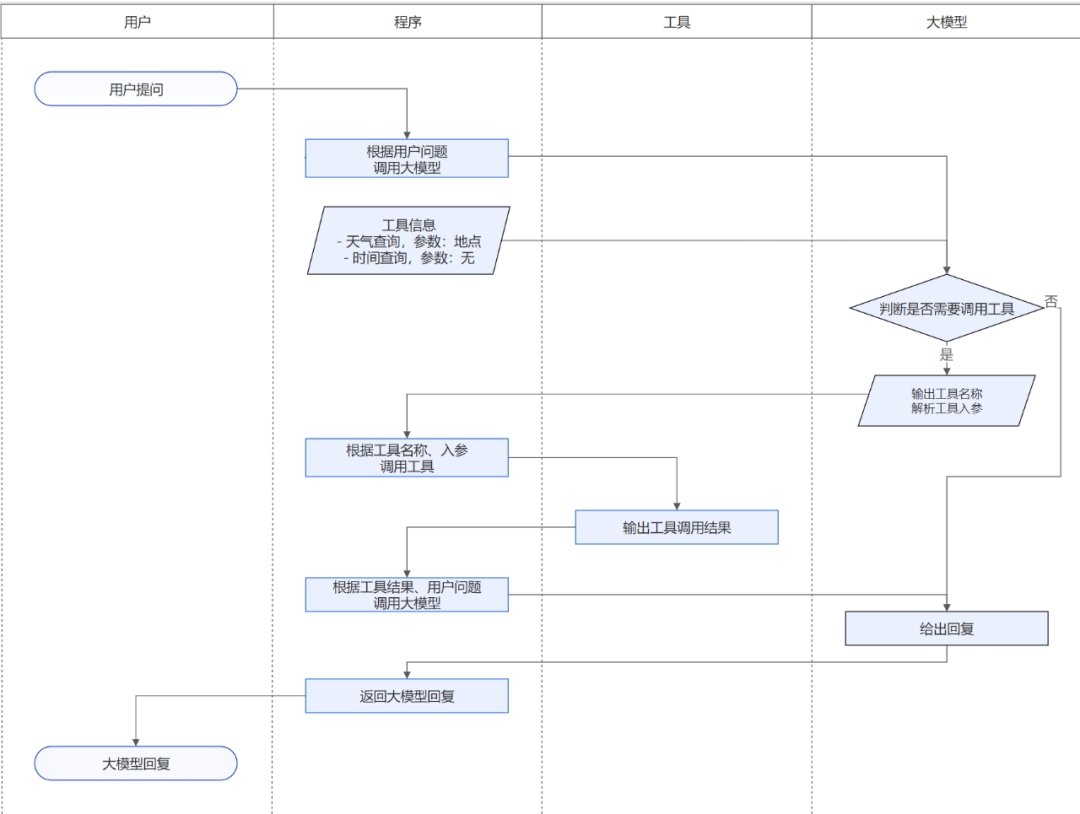
注:该图来源于千问模型官网
背景也交代完了,下面我们就直接开始教程吧。
一、通过官方例子实现from dashscope import Generation
from datetime import datetime
import random
# 定义工具列表,模型在选择使用哪个工具时会参考工具的name和description
tools = [
# 工具1 获取当前时刻的时间
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_time",
"description": "当你想知道现在的时间时非常有用。",
"parameters": {} # 因为获取当前时间无需输入参数,因此parameters为空字典
}
},
# 工具2 获取指定城市的天气
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "当你想查询指定城市的天气时非常有用。",
"parameters": { # 查询天气时需要提供位置,因此参数设置为location
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市或县区,比如北京市、杭州市、余杭区等。"
}
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
# 模拟天气查询工具。返回结果示例:“北京今天是晴天。”
def get_current_weather(location):
return f"{location}今天是晴天。 "
# 查询当前时间的工具。返回结果示例:“当前时间:2024-04-15 17:15:18。“
def get_current_time():
# 获取当前日期和时间
current_datetime = datetime.now()
# 格式化当前日期和时间
formatted_time = current_datetime.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# 返回格式化后的当前时间
return f"当前时间:{formatted_time}。"
# 封装模型响应函数
def get_response(messages):
response = Generation.call(
model='qwen-turbo',
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
api_key="申请的qwen-api-key",
seed=random.randint(1, 10000), # 设置随机数种子seed,如果没有设置,则随机数种子默认为1234
result_format='message' # 将输出设置为message形式
)
return response
def call_with_messages():
messages = [
{
"content": input('请输入问题:'), # 提问示例:"现在几点了?" "一个小时后几点" "北京天气如何?"
"role": "user"
}
]
# 模型的第一轮调用
assistant_output = get_response(messages).output.choices[0].message
print("返回的消息:")
print(assistant_output)
messages.append(assistant_output)
if 'tool_calls' not in assistant_output: # 如果模型判断无需调用工具,则将assistant的回复直接打印出来,无需进行模型的第二轮调用
print(assistant_output.content)
return
# 如果模型选择的工具是get_current_weather
elif assistant_output.tool_calls[0]['function']['name'] == 'get_current_weather':
tool_info = {"name": "get_current_weather", "role":"tool"}
location = assistant_output.tool_calls[0]['function']['arguments']
print(f"调用天气的参数:{location}")
tool_info['content'] = get_current_weather(location)
# 如果模型选择的工具是get_current_time
elif assistant_output.tool_calls[0]['function']['name'] == 'get_current_time':
tool_info = {"name": "get_current_time", "role":"tool"}
tool_info['content'] = get_current_time()
messages.append(tool_info)
print(messages)
# 模型的第二轮调用,对工具的输出进行总结
response = get_response(messages)
print(f"模型回复:{response.output.choices[0].message['content']}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
call_with_messages()
二、通过langchain实现langchain中最常使用的是通过bind_tools方法(注:以下代码不能直接运行)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125")
tools = [multiply, exponentiate, add]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools) 目前langchain中qwen模型没有提供该bind_tools,所以我们不能通过该方式直接调用。不过,好消息的是,已经看到有人提交了合并请求,在后续版本中应该就可以用该方法直接调用工具了。
ChatTongyi中的bind(tools=tools)方式,具体代码如下
from langchain_core.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate
)
from langchain_core.messages import (
HumanMessage,
FunctionMessage
)
# from langchain_community.llms import Tongyi
from langchain_community.chat_models.tongyi import ChatTongyi
import os
qwen_api_key = "申请的qwen-api-key"
os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"] = qwen_api_key 定义工具参数和方法 tools = [
# 工具1 获取当前时刻的时间
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_time",
"description": "当你想知道现在的时间时非常有用。",
"parameters": {} # 因为获取当前时间无需输入参数,因此parameters为空字典
}
},
# 工具2 获取指定城市的天气
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "当你想查询指定城市的天气时非常有用。",
"parameters": { # 查询天气时需要提供位置,因此参数设置为location
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市或县区,比如北京市、杭州市、余杭区等。"
}
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
# 模拟天气查询工具。返回结果示例:“北京今天是晴天。”
def get_current_weather(location):
return f"{location}今天是晴天。 "
# 查询当前时间的工具。返回结果示例:“当前时间:2024-04-15 17:15:18。“
def get_current_time():
formatted_time = "2024年4月25日22:10:32"
# 返回格式化后的当前时间
return f"当前时间:{formatted_time}。" 开始调用 chat = ChatTongyi(model="qwen-plus")
prompt_tmpl = "使用给定函数回答下列问题 {input}"
prompt_msgs = [
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_tmpl),
]
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate(messages=prompt_msgs)
# 绑定我们定义的工具配置
chain = prompt | chat.bind(tools=tools)
message = HumanMessage(content="上海的天气?")
response = chain.batch([{"input": message}])
response 我们看看返回的参数,已经有调用天气的函数了。tool_calls中get_current_weather [AIMessage(content='',additional_kwargs={'tool_calls':[{'function':{'name':'get_current_weather','arguments':'{"properties":{"location":{"description":"上海市","type":"string"}}}'},'id':'','type':'function'}]},response_metadata={'model_name':'qwen-plus','finish_reason':'tool_calls','request_id':'e65c3092-78c6-90ef-89f0-d2b4dcf0472f','token_usage':{'input_tokens':233,'output_tokens':31,'total_tokens':264}},id='run-5d225659-082b-4e45-9ffa-18dc61eb268a-0',tool_calls=[{'name':'get_current_weather','args':{'properties':{'location':{'description':'上海市','type':'string'}}},'id':''}])]后续可以参考官方的例子,拿到方法名称,直接调用对应的方法就好了。 |