ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;">文本嵌入和矢量相似性搜索可以帮助我们理解文档的含义以及它们之间的相似程度,从而找到文档。但是,当根据日期或类别等特定条件对信息进行排序时,文本嵌入就不那么有效了;例如,如果你需要查找在某一年创建的所有文档,或者在 "科幻小说 "等特定类别下标记的文档。这就是元数据过滤或过滤矢量搜索发挥作用的地方,因为它可以有效地处理这些结构化过滤器,让用户根据特定属性缩小搜索结果的范围。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;"> 在所提供的图片中,流程开始时,用户会询问是否有新政策在 2021 年实施。然后使用元数据过滤器,按照指定年份(本例中为 2021 年)对索引文件池中的大量文件进行排序。这样就能得到仅来自该年的经过过滤的文档子集。为了进一步筛选出最相关的文档,我们在这个子集中进行了向量相似性搜索。通过这种方法,系统可以从 2021 年的相关文档库中找到与感兴趣的主题密切相关的文档。元数据过滤和矢量相似性搜索这两个步骤提高了搜索结果的准确性和相关性。最近,我们在 Neo4j 中引入了基于节点属性的 LangChain 元数据过滤支持。然而,像Neo4j[1]这样的图数据库可以存储高度复杂和连接的结构化数据以及非结构化数据。让我们看看下面的例子: 在所提供的图片中,流程开始时,用户会询问是否有新政策在 2021 年实施。然后使用元数据过滤器,按照指定年份(本例中为 2021 年)对索引文件池中的大量文件进行排序。这样就能得到仅来自该年的经过过滤的文档子集。为了进一步筛选出最相关的文档,我们在这个子集中进行了向量相似性搜索。通过这种方法,系统可以从 2021 年的相关文档库中找到与感兴趣的主题密切相关的文档。元数据过滤和矢量相似性搜索这两个步骤提高了搜索结果的准确性和相关性。最近,我们在 Neo4j 中引入了基于节点属性的 LangChain 元数据过滤支持。然而,像Neo4j[1]这样的图数据库可以存储高度复杂和连接的结构化数据以及非结构化数据。让我们看看下面的例子:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; font-size: 15px; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; margin-top: 10px; margin-bottom: 10px;">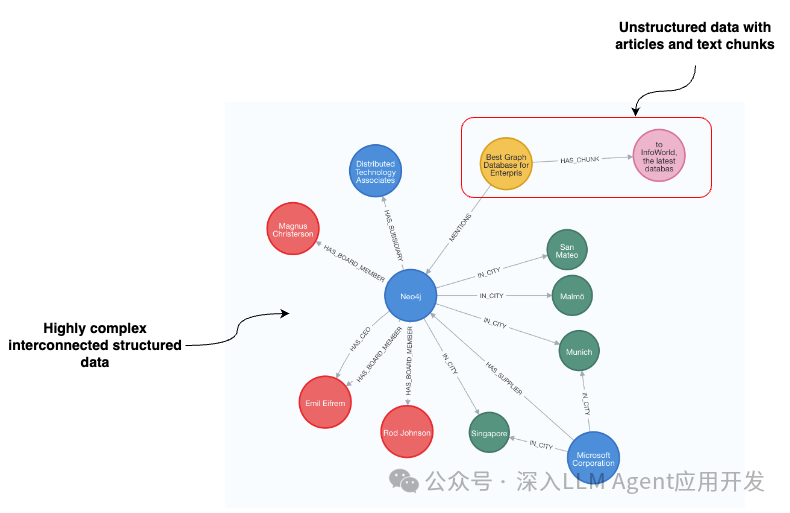 ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; font-size: 15px; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal;">在罗德-约翰逊担任董事会成员的公司中,有哪家公司实施了新的在家办公政策?对于为现代汽车供货的公司来说,是否有与供应链问题有关的值得注意的新闻?通过所有这些示例问题,您可以使用基于结构图的元数据过滤器大大缩小相关文档子集的范围。在这篇博文中,我将向大家展示如何使用 LangChain 结合 OpenAI 函数调用代理实现基于图的元数据过滤。代码可在GitHub[2]上获取。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; min-height: 32px; line-height: 28px; color: rgb(119, 48, 152); border-bottom: 1px solid rgb(119, 48, 152); border-top-color: rgb(119, 48, 152); border-right-color: rgb(119, 48, 152); border-left-color: rgb(119, 48, 152); font-size: 22px; margin: 1em auto; padding-top: 0.5em; padding-bottom: 0.5em; text-align: center; width: 367.617px; display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center;">1. 准备数据集ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;">我们将使用 Neo4j 托管的公共演示服务器上的所谓公司图数据集。您可以使用以下凭据访问该数据集。Neo4j Browser URI: https://demo.neo4jlabs.com:7473/browser/
username: companies
password: companies
database: companies
ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;">数据集的完整模式如下:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;"> 图模式围绕组织节点展开。有大量关于其供应商、竞争对手、地理位置、董事会成员等方面的信息。如前所述,还有一些文章提到了特定的组织及其相应的文本块。我们将用一个工具来实现 OpenAI 代理,它可以根据用户输入动态生成 Cypher 语句,并从图数据库中检索相关文本块。在本示例中,该工具将有四个可选输入参数:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; font-size: 15px; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal;">主题:除组织、国家和情感外,用户感兴趣的任何特定信息或主题。国家:用户感兴趣的组织所在国家。使用全称,如美国和法国。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;">根据四个输入参数,我们将动态但确定地构建相应的 Cypher 语句,从图形中检索相关信息,并将其作为上下文,使用 LLM 生成最终答案。您将需要一个 OpenAI API 密钥来跟进代码。 图模式围绕组织节点展开。有大量关于其供应商、竞争对手、地理位置、董事会成员等方面的信息。如前所述,还有一些文章提到了特定的组织及其相应的文本块。我们将用一个工具来实现 OpenAI 代理,它可以根据用户输入动态生成 Cypher 语句,并从图数据库中检索相关文本块。在本示例中,该工具将有四个可选输入参数:ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; font-size: 15px; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal;">主题:除组织、国家和情感外,用户感兴趣的任何特定信息或主题。国家:用户感兴趣的组织所在国家。使用全称,如美国和法国。ingFang SC", Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif; letter-spacing: 0.75px; white-space: normal; padding-top: 8px; padding-bottom: 8px; line-height: 26px;">根据四个输入参数,我们将动态但确定地构建相应的 Cypher 语句,从图形中检索相关信息,并将其作为上下文,使用 LLM 生成最终答案。您将需要一个 OpenAI API 密钥来跟进代码。2. 功能实现我们将从定义凭证和与 Neo4j 的相关连接开始。 importos
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]="sk-"
os.environ["NEO4J_URI"]="neo4j+s://demo.neo4jlabs.com"
os.environ["NEO4J_USERNAME"]="companies"
os.environ["NEO4J_PASSWORD"]="companies"
os.environ["NEO4J_DATABASE"]="companies"
embeddings=OpenAIEmbeddings()
graph=Neo4jGraph()
vector_index=Neo4jVector.from_existing_index(
embeddings,
index_name="news"
)
如前所述,我们将使用 OpenAI 嵌入,为此需要其 API 密钥。接下来,我们定义与 Neo4j 的图连接,这样就可以执行任意的 Cypher 语句。最后,我们实例化一个 Neo4jVector 连接,它可以通过查询现有的向量索引来获取信息。在撰写本文时,您不能将矢量索引与预过滤方法结合使用;您只能将后过滤与矢量索引结合使用。不过,关于后过滤的讨论超出了本文的讨论范围,因为我们将重点讨论结合详尽的向量相似性搜索的预过滤方法。或多或少,整篇博文可以归结为以下get_organization_news函数,该函数动态生成 Cypher 语句并检索相关信息。为清晰起见,我将把代码分成多个部分。 defget_organization_news(
topic:Optional[str]=None,
organization:Optional[str]=None,
country:Optional[str]=None,
sentiment:Optional[str]=None,
)->str:
#Ifthereisnoprefiltering,wecanusevectorindex
iftopicandnotorganizationandnotcountryandnotsentiment:
returnvector_index.similarity_search(topic)
#Usesparallelruntimewhereavailable
base_query=(
"CYPHERruntime=parallelparallelRuntimeSupport=all"
"MATCH(c:Chunk)<-[:HAS_CHUNK]-(a:Article)WHERE"
)
where_queries=[]
params={"k":5}#Definethenumberoftextchunkstoretrieve
我们首先定义输入参数。正如你所看到的,所有参数都是可选字符串。主题参数用于查找文档中的特定信息。在实践中,我们会嵌入主题参数的值,并将其作为向量相似性搜索的输入。其他三个参数将用于演示预过滤方法。如果所有预过滤参数都为空,我们就可以使用现有的向量索引找到相关文档。否则,我们就开始准备将用于预过滤元数据方法的基础 Cypher 语句。CYPHER runtime = parallel parallelRuntimeSupport=all子句指示 Neo4j 数据库在可用的情况下使用并行运行时。接下来,我们准备一个匹配语句,选择 Chunk 节点及其对应的文章节点。现在,我们可以在 Cypher 语句中动态附加元数据过滤器了。我们将从 Organizationfilter 开始。 iforganization:
#Maptodatabase
candidates=get_candidates(organization)
iflen(candidates)>1:#Askforfollowupiftoomanyoptions
return(
"Askafollowupquestionwhichoftheavailableorganizations"
f"didtheusermean.Availableoptions:{candidates}"
)
where_queries.append(
"EXISTS{(a)-[:MENTIONS]->(:Organization{name organization})}" organization})}"
)
params["organization"]=candidates[0]
如果 LLM 识别出用户感兴趣的任何特定组织,我们必须首先使用 get_candidates 函数将该值映射到数据库。在引擎盖下,get_candidates 函数利用[全文索引进行关键词搜索](<(https://neo4j.com/docs/cypher-manual/current/indexes/semantic-indexes/full-text-indexes/ "全文索引进行关键词搜索")>),以找到候选节点。如果找到多个候选节点,我们会指示 LLM 向用户提出一个后续问题,以明确他们到底指的是哪个组织。否则,我们会在过滤器列表中添加一个存在子查询[3],过滤提及特定组织的文章。为了防止任何 Cypher 注入,我们使用查询参数而不是连接查询。接下来,我们将处理用户希望根据所提及组织的国家预先过滤文本块的情况。 ifcountry:
#Noneedtodisambiguate
where_queries.append(
"EXISTS{(a)-[:MENTIONS]->(:Organization)-[:IN_CITY]->()-[:IN_COUNTRY]->(:Country{name country})}" country})}"
)
params["country"]=country
由于国家遵循标准命名,我们不必将数值映射到数据库中,因为法律硕士熟悉大多数国家的命名标准。同样,我们也处理情感元数据过滤。 ifsentiment:
ifsentiment=="positive":
where_queries.append("a.sentiment>$sentiment")
params["sentiment"]=0.5
else:
where_queries.append("a.sentiment<$sentiment")
params["sentiment"]=-0.5
我们将指示 LLM 对情感输入值只使用两个值,即正值或负值。然后,我们将这两个值映射到适当的过滤值。我们对 topic 参数的处理略有不同,因为它不是用于预过滤,而是用于向量相似性搜索。 iftopic:#Dovectorcomparison
vector_snippet=(
"WITHc,a,vector.similarity.cosine(c.embedding,$embedding)ASscore"
"ORDERBYscoreDESCLIMITtoInteger($k)"
)
params["embedding"]=embeddings.embed_query(topic)
else:#Justreturnthelatestdata
vector_snippet="WITHc,aORDERBYa.dateDESCLIMITtoInteger($k)"
如果 LLM 识别出用户对新闻中的某个特定主题感兴趣,我们就会使用主题输入的文本嵌入来查找最相关的文档。另一方面,如果没有识别出特定的主题,我们只需返回最新的几篇文章,完全避免矢量相似性搜索。现在,我们必须将 Cypher 语句组合在一起,用它从数据库中获取信息。 return_snippet="RETURN'#title'+a.title+'\n#date'+toString(a.date)+'\n#text'+c.textASoutput"
complete_query=(
base_query+"AND".join(where_queries)+vector_snippet+return_snippet
)
#Retrieveinformationfromthedatabase
data=graph.query(complete_query,params)
print(f"Cypher:{complete_query}\n")
#Safelyremoveembeddingbeforeprinting
params.pop('embedding',None)
print(f"Parameters:{params}")
return"###Article:".join([el["output"]forelindata])
我们通过组合所有查询片段来构建最终的 complete_query。然后,我们使用动态生成的 Cypher 语句从数据库中检索信息,并将其返回给 LLM。让我们以输入为例,检查生成的 Cypher 语句。 get_organization_news(
organization='neo4j',
sentiment='positive',
topic='remotework'
)
#Cypher:CYPHERruntime=parallelparallelRuntimeSupport=all
#MATCH(c:Chunk)<-[:HAS_CHUNK]-(a:Article)WHERE
#EXISTS{(a)-[:MENTIONS]->(:Organization{name organization})}AND organization})}AND
#a.sentiment>$sentiment
#WITHc,a,vector.similarity.cosine(c.embedding,$embedding)ASscore
#ORDERBYscoreDESCLIMITtoInteger($k)
#RETURN'#title'+a.title+'\ndate'+toString(a.date)+'\ntext'+c.textASoutput
#Parameters:{'k':5,'organization':'Neo4j','sentiment':0.5}
动态查询生成功能符合预期,能够从数据库中检索到相关信息。 3. 定义 OpenAI 代理接下来,我们需要将该函数包装成一个 Agent 工具。首先,我们将添加输入参数说明。 fewshot_examples="""{Input:WhatarethehealthbenefitsforGoogleemployeesinthenews?Query:Healthbenefits}
{Input:WhatisthelatestpositivenewsaboutGoogle?Query:None}
{Input:ArethereanynewsaboutVertexAIregardingGoogle?Query:VertexAI}
{Input:ArethereanynewsaboutnewproductsregardingGoogle?Query:newproducts}
"""
classNewsInput(BaseModel):
topic:Optional[str]=Field(
description="Anyspecificinformationortopicbesidesorganization,country,andsentimentthattheuserisinterestedin.Herearesomeexamples:"
+fewshot_examples
)
organization:Optional[str]=Field(
description="Organizationthattheuserwantstofindinformationabout"
)
country:Optional[str]=Field(
description="Countryoforganizationsthattheuserisinterestedin.UsefullnameslikeUnitedStatesofAmericaandFrance."
)
sentiment:Optional[str]=Field(
description="Sentimentofarticles",enum=["positive","negative"]
)
预过滤参数的描述非常简单,但我在让主题参数按预期工作时遇到了一些问题。最后,我决定添加一些示例,以便 LLM 能够更好地理解。此外,您还可以看到,我们向 LLM 提供了有关国家命名格式的信息,并提供了情感的枚举。现在,我们可以定义一个自定义工具,给它一个名称和描述,其中包含 LLM 使用说明。 classNewsTool(BaseTool):
name="NewsInformation"
description=(
"usefulforwhenyouneedtofindrelevantinformationinthenews"
)
args_schema:Type[BaseModel]=NewsInput
def_run(
self,
topic:Optional[str]=None,
organization:Optional[str]=None,
country:Optional[str]=None,
sentiment:Optional[str]=None,
run_manager:Optional[CallbackManagerForToolRun]=None,
)->str:
"""Usethetool."""
returnget_organization_news(topic,organization,country,sentiment)
最后一件事是定义代理执行器。我只是重复使用了前段时间实现的 OpenAI 代理的 [LCEL 实现](<(https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/ "LCEL 实现")>)。 llm=ChatOpenAI(temperature=0,model="gpt-4-turbo",streaming=True)
tools=[NewsTool()]
llm_with_tools=llm.bind(functions=[format_tool_to_openai_function(t)fortintools])
prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"Youareahelpfulassistantthatfindsinformationaboutmovies"
"andrecommendsthem.Iftoolsrequirefollowupquestions,"
"makesuretoasktheuserforclarification.Makesuretoincludeany"
"availableoptionsthatneedtobeclarifiedinthefollowupquestions"
"Doonlythethingstheuserspecificallyrequested.",
),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
("user","{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad"),
]
)
agent=(
{
"input":lambdax:x["input"],
"chat_history":lambdax:_format_chat_history(x["chat_history"])
ifx.get("chat_history")
else[],
"agent_scratchpad":lambdax:format_to_openai_function_messages(
x["intermediate_steps"]
),
}
|prompt
|llm_with_tools
|OpenAIFunctionsAgentOutputParser()
)
agent_executor=AgentExecutor(agent=agent,tools=tools)
代理只需使用一个工具就能检索新闻信息。我们还添加了 chat_history 消息占位符,使代理可以进行对话,并允许后续提问和回复。 4. 测试让我们运行几个输入,检查生成的 Cypher 语句和参数。 agent_executor.invoke(
{"input":"Whataresomepositivenewsregardingneo4j?"}
)
#Cypher:CYPHERruntime=parallelparallelRuntimeSupport=all
#MATCH(c:Chunk)<-[:HAS_CHUNK]-(a:Article)WHERE
#EXISTS{(a)-[:MENTIONS]->(:Organization{name organization})}AND organization})}AND
#a.sentiment>$sentimentWITHc,a
#ORDERBYa.dateDESCLIMITtoInteger($k)
#RETURN'#title'+a.title+'date'+toString(a.date)+'text'+c.textASoutput
#Parameters:{'k':5,'organization':'Neo4j','sentiment':0.5}
生成的 Cypher 语句是有效的。由于我们没有指定任何特定主题,因此它返回了提及 Neo4j 的正面文章中的最后五个文本块。让我们做一些更复杂的事情: agent_executor.invoke(
{"input":"WhataresomeofthelatestnegativenewsaboutemployeehappinessforcompaniesfromFrance?"}
)
#Cypher:CYPHERruntime=parallelparallelRuntimeSupport=all
#MATCH(c:Chunk)<-[:HAS_CHUNK]-(a:Article)WHERE
#EXISTS{(a)-[:MENTIONS]->(:Organization)-[:IN_CITY]->()-[:IN_COUNTRY]->(:Country{name country})}AND country})}AND
#a.sentiment<$sentiment
#WITHc,a,vector.similarity.cosine(c.embedding,$embedding)ASscore
#ORDERBYscoreDESCLIMITtoInteger($k)
#RETURN'#title'+a.title+'date'+toString(a.date)+'text'+c.textASoutput
#Parameters:{'k':5,'country':'France','sentiment':-0.5,'topic':'employeehappiness'}
LLM 代理不仅能正确生成预过滤参数,还能识别特定的员工幸福感主题。该主题被用作矢量相似性搜索的输入,使我们能够进一步完善检索过程。 5. 总结在这篇博文中,我们实施了基于图的元数据过滤器示例,从而提高了矢量搜索的准确性。然而,数据集具有广泛且相互关联的选项,可以进行更复杂的预过滤查询。通过图数据表示,结合 LLM 函数调用功能动态生成 Cypher 语句,结构化过滤器的可能性几乎是无限的。此外,您的代理还可以拥有检索非结构化文本的工具(如本博文所示),以及检索结构化信息[4]的其他工具,从而使知识图谱成为许多 RAG 应用程序的出色解决方案。
|